NEWS AND COMMENTS
Declaring the transport of dangerous goods - an additional security guarantee...
Pre-shipment inspection of tank containers intended for the carriage of dangerous goods...
ISTC started training experts...
Preparation for the XIV International Conference "Multimodal Transport of Dangerous Goods"...
Training of specialists in a new quality...
"Sea Trade Port "Ust-Luga" JSC has successfully passed the certification audit...
IDGCA presents Russian version of the IMDG Code latest edition on disks...
An IMO circular does not define competency of national authorities...
XIII International Conference ´┐ŻMulti-modal transportation of dangerous goods´┐Ż...
An IMO circular does not define responsibilities and authority of national organizations...
11th Session of the IMO Sub-Committee on the Carriage of Cargoes and Containers | 24.09.2025 |
|---|---|
  
The 11th session of the Sub-Committee on Carriage of Cargoes and Containers (CCC) was held from 8 to 12 September at the International Maritime Organization (IMO) headquarters in London. The session approved draft IMO guidelines on the safety of ships using hydrogen and liquid ammonia as fuel. These important draft guidelines are scheduled for approval in May 2026 at the 111th session of the Maritime Safety Committee (MSC). The transition to low-flashpoint marine fuel grades entails changes to ship construction and equipment requirements, which will naturally impose additional costs on ship owners. The Sub-Committee completed its work on a package of amendments to the International Code for the Construction and Equipment of Ships Carrying Liquefied Gases in Bulk (IGC Code). Implementation of these amendments will allow ships carrying liquefied gases in bulk to use these gases as fuel for their main engines. This expands the range of gases that can be transported as cargo but also be used as marine fuel. Despite the international community's efforts to prevent container loss, both during maritime transport and during port cargo operations, the Subcommittee once again drew attention to this problem and proposed amendments to the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS-74) and several other IMO instruments. This follows a number of container loss incidents, including those containing dangerous goods, which pose a significant environmental hazard. The latest confirmation of the need to improve container loss prevention was the incident that occurred on the eve of the session, when 67 containers fell from the container ship Mississippi during cargo operations at a terminal in the Californian port of Long Beach (USA) on September 9. IMO experts approved a number of editorial amendments, as well as new requirements for the carriage of specific types of cargo, for subsequent inclusion in the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code and the International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargoes (IMBC) Code. The Subcommittee is currently preparing a new version of the IMDG Code, taking into account amendments 43-26. This version will be adopted in 2026 and enter into force on 1 January 2028. It is important to note that all significant changes to the IMDG Code concerning the carriage of dangerous goods, containers, and packaging for them are initially discussed by the UN ECOSOC Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. A standing group, comprising experts from both this Sub-Committee and the IMO Sub-Committee on the Carriage of Goods and Containers, monitors all expert proposals from both the UN and IMO. It should be noted that the proposals of the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (IDGCA), adopted by the UN ECOSOC Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, are subsequently seamlessly integrated into the requirements of the IMDG Code, although certain changes related to the specifics of maritime transport are possible. Previously, before 2010, the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association, represented by its Director General, M.I. Ognev, actively participated in the work of the IMO Sub-Committee on the Transport of Dangerous Goods and Containers. IMO Secretary-General E. Mitropoulos personally allocated time to exchange views on issues related to the transport of dangerous goods and containers with M.I. Ognev. Both the IMO Sub-Committee on the Transport of Dangerous Goods and Containers and the UN ECOSOC Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, as well as other UN sectoral structures, place special emphasis on the training of personnel involved in the transport of dangerous goods. Competent, trained personnel are the key to the safe transport of dangerous goods and all work involving them. Large companies place special emphasis on personnel training, sending their specialists to the International Staff Training Center (ISTC), a subsidiary of the IDGCA NP. The next training courses for specialists in loading and unloading operations related to dangerous goods will be held at the ISTC from October 6 to 10. | |
New national standard for Russian business | 08.07.2025 |
 
Specialists from the National Bureau of Expertise Ltd., together with experts from the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (IDGCA NP), have developed and submitted for approval to the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology (Rosstandart) the first edition of the national standard of the Russian Federation "Portable tanks for the transportation of refrigerated liquefied gases ÔÇô General technical requirements." The project is being developed in accordance with the National Standards Development Program for 2025 (subject code: 1.2.114-1.033.25). This project takes into account the provisions of basic international documents:
Both international rules for the transportation of dangerous goods and international standards for cryogenic vessels are being developed with the direct participation of experts from the IDGCA NP working in the UN ECOSOC Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods and the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals, as well as in the Technical Committee of the International Standardization Organization, ISO TC 220 ÔÇô Cryogenic vessels. This standard, which has no analogues not only in Russia but also in the world, will be the basis for the development of a family of standards, both national and international, the implementation of which will significantly increase the reliability of the manufactured transport equipment for the transportation of dangerous goods and the profitability of transportation. Based on this standard, domestic enterprises will have the opportunity to develop and manufacture a wide range of portable tanks, including tank containers, swap body tanks and their modifications, which will be worthy competitors in the world market of equipment designed for the transportation of dangerous goods. | |
Training of specialists in the field chartering of vessels | 04.07.2025 |

Chartering of sea and river vessels is a multifaceted, complex process of choosing a specific vessel for cargo delivery, taking into account the crew, choosing an insurance company and solving many other issues. The organization of transportation on a chartered vessel has its own specifics and rules that should not be neglected by either charterers or ship owners. Failure to comply with the rules can result in serious problems and unplanned expenses. A chartering specialist must have strong skills in quickly finding mutually beneficial options. In addition, to participate in the maritime transportation market, specialists must have deep knowledge of the maritime legislation of the Russian Federation and international legislation, as well as the practice of chartering ships, navigation safety, insurance, interaction with classification societies and administrations. From June 23 to 27, 2025, the International Staff Training Center held regular courses on chartering of vessels for managers of the FESCO shipping company. Along with the standard requirements for training chartering specialists, the students received knowledge in the field of International Conventions, Codes and Agreements. The invited teachers included lawyers with experience in litigation between the ship owner and the insurer, heads of the Ingosstrakh insurance department, customs specialists, experts in the field of classification and inspection of ships and other specialists, and highly qualified teachers who supplemented the students' knowledge with relevant information. FESCO specialists expressed gratitude for organizing the courses and made suggestions for the future. | |
Regular session of technical committee ISO/TC 220 ÔÇô Cryogenic vessels | 30.06.2025 |
 
Experts of the IDGCA NP took part in the regular plenary session of the technical committee of the International Organization for Standardization ISO/TC 220 ÔÇô Cryogenic vessels, which was held on June 26, 2025 at the headquarters of the French Association for Standardization (AFNOR). During the plenary session, the editorial committee was appointed, the report on the implementation of the decisions of the previous plenary session was approved, and the report of the secretariat of the technical committee was heard. The issues of implementation of the ISO Code of Ethics and Conduct were discussed and the Strategic Business Plan of the committee was reviewed. The participants of the plenary session were greatly interested in the information about the use of the platform for online standards development (OSD). The OSD platform has a number of advantages over traditional tools such as Word, it provides transparency of information and the ability to track the progress of document development and make proposals and amendments to it. Changes are made securely online, with the ability to block and unblock sections to eliminate the possibility of unfair use of the material. The participants of the plenary session heard the reports of the working groups, which concerned the improvement of a number of ISO standards. Based on the results of the session, 4 resolutions were adopted. The work of the experts of the IDGCA NP in the technical committee ISO/TC 220, including participation in its plenary sessions since 2004, significantly helps to solve the problems of both the Association itself and its subsidiaries. Thus, the latest information concerning the development of cryogenic technology is successfully used in the educational process of the International Staff Training Center, in particular, in the training of loading masters and loading operators of LNG terminals. Taking into account the provisions of a number of international standards, in the development of which experts from the IDGCA NP took part, specialists from National Bureau of Expertise Ltd. developed and submitted for approval to the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology (Rosstandart) the first edition of the national standard of the Russian Federation "Portable tanks for transportation of refrigerated liquefied gases. General technical requirements". The draft is being developed in accordance with the National Standardization Program for 2025 (subject code: 1.2.114-1.033.25). Based on this standard, domestic enterprises will have the opportunity to develop and manufacture a wide range of portable tanks, including tank containers, swap body tanks and their modifications, which will compete in the global market for equipment designed for the transportation of dangerous goods. | |
Technical regulation is the basis for ensuring safety during the transportation of dangerous goods | 24.06.2025 |

On June 17, the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (IDGCA) held a seminar on Technical Regulation In The Field of Transportation of Dangerous Goods by Sea Transport, In Seaports And Terminals. The seminar was opened and the report was made by the President of the IDGCA Moshkov G. Yu. He covered in detail the state of affairs in the field of technical regulation in sea and river ports, pointing out the problems that need to be addressed in this area in the nearest future. First of all, this concerns the need to improve the national regulatory framework and harmonize it with the international one, which seems to be a rather complex problem, the solution of which should in no case be reduced to the mechanical transfer of the provisions of international documents to national regulatory legal acts. The speaker noted the important role that the IDGCA NP plays in the processes of technical regulation both at the national and international levels. The report examined in detail the issues related to ensuring anti-terrorist protection of maritime transport and transport infrastructure, where special attention should be paid to handling high-consequence dangerous goods ÔÇô cargo that can be used by terrorists to achieve their goals. The speaker emphasized that regulations governing the transportation of dangerous goods and all types of work with them must be justified, meet the requirements of national legislation, reflect and protect the interests of business and prevent abuses in the control of its activities, and contribute to the creation of conditions for healthy competition. In their speeches, the participants of the seminar expressed their opinions on the essence of the issues on the agenda of the event. Executive Secretary of the National Technical Committee for Standardization TC 114 "Oxygen and Cryogenic Equipment", E.V. Demidova, and GOST R Administrator, the Head of the Department for Interaction with ISO, A.V. Deryabina familiarized the seminar participants with the implementation of the National Standardization Program (NSP) for 2025, approved by order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology dated October 31, 2024 Ôäľ 2596, and the interaction of national standardization committees with ISO technical committees. At the same time, it was emphasized that the experts of the National Bureau of Expertise Ltd., together with the experts of the IDGCA NP, as part of the implementation of the NSP for 2025, developed and submitted for approval a draft national standard "Portable tanks for the transportation of refrigerated liquefied gases. General technical requirements", the adoption of which will open up great opportunities for the creation of new types of promising equipment for the transportation of refrigerated liquefied gases. The speech of the representative of the Murmansk Association of Captains, sea captain, Dmitrievsky V.D., was devoted to the analysis of the practice of applying international conventions, codes and guidelines in the interaction "vessel-terminal". The speakers paid much attention to the draft of the new technical regulation "On the safety of marine transport facilities", as well as proposals to amend the Merchant Shipping Code of the Russian Federation dated April 30, 1999 Ôäľ 81-FZ, and emphasized that these documents have not received due public discussion, as a result of which their adoption in their current form may have an unsatisfactory effect on the work of businesses and the activities of supervisory and control bodies. The fundamental problems of interaction between sea and rail transport in the transportation of dangerous goods were touched upon in the speech of the representative of Emperor Alexander I St. Petersburg State Transport University, Fedorov I.V., who noted that there are still no rules for the transportation of railway tanks on ferries that would meet the standards established for both sea and rail transport. These speeches and speeches of other participants in the seminar, as well as the round table that took place, made it possible to develop and adopt the Resolution of the seminar. The opinions expressed by the speakers and participants of the seminar showed that to date there is no harmonization between national and international legislation in the Russian Federation. The seminar was attended by officials of the Directorate for State of Maritime and River Supervision of the Federal Service for Supervision of Transport, as well as its interregional territorial departments in all federal districts of the Russian Federation, the Federal Service for Environmental, Technological and Nuclear Supervision, members of ÔÇťStandardization InstituteÔÇŁ Federal State Budgetary Institution, representatives of the Russian Maritime Register of Shipping, representatives of business, universities and public organizations. | |
Chemistry is a force that must be controlled | 29.05.2025 |

On May 27, a massive explosion occurred at a chemical plant located in the city of Gaomi in Shandong Province in eastern China. The incident occurred in the workshop of Shandong Gaomi Youdao Chemical Co., Ltd. The company is the world's largest manufacturer of the pesticide chlorpyrifos and produces about 11 thousand tons of this product per year. Journalists note that five people died as a result of the explosion. It is also reported that six people are missing and 19 are injured. 232 rescuers and 55 pieces of equipment were sent to the scene of the incident, and national fire and rescue teams with equipment for responding to emergency situations at industrial facilities were involved in eliminating the consequences of the explosion. Chlorpyrifos is a widely used organophosphate pesticide that is used to control pests in agriculture. But this substance poses significant risks to human health and the environment. Its use can lead to contamination of soil and water resources, threatening biodiversity and aquatic ecosystems. In addition, it is highly toxic to humans and can cause problems with the nervous system, respiratory tract and skin. Agricultural workers and consumers of agricultural products may be at risk of poisoning if the pesticide is used incorrectly. According to some experts, based on the chemical composition of chlorpyrifos and the circumstances of the explosion, in particular the formation of a high-temperature fireball, the incident could have released very dangerous compounds dioxins and furans, and they can spread over large distances due to atmospheric transport. Dioxins and related furans are a group of chemical compounds with more than two hundred names, of which seventeen are extremely dangerous to humans and the environment. Various incidents are associated with these substances, and the largest known was the catastrophe in which tetrachlorodibenzodioxin leaked at a chemical plant near the city of Seveso in northern Italy on July 10, 1976. Then, in a few minutes, about 2 kilograms of dioxins were released from the chemical reactor. This amount is enough to kill about 100 thousand people. The causes of the disaster in Gaomi County will be investigated, but it is already possible to note that, judging by the video materials published on the Internet, a worker was on the roof of the tank moments before its explosion, and, as one can judge, without personal protective equipment. Most likely, the notorious "human factor" was again involved in this incident, when the qualifications of the personnel do not correspond to the level of complexity and responsibility of the functions performed. The risk of accidents in chemical production, as well as in transport during the transportation of chemicals, can be significantly reduced only through continuous training of managers and employees of enterprises. This is also indicated by the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals, which defines a risk indicator as the product of the hazard index of a chemical product and the probability of its negative impact. The probability of a negative impact of a chemical product is directly related to the level of professionalism of the personnel. | |
Container ship carrying dangerous cargo under Liberian flag sank off the coast of India | 27.05.2025 |
 
The container ship MSC ELSA 3 carrying dangerous chemical cargo sank 38 nautical miles off the coast of India, southwest of the port city of Cochin (Kerala). All 24 crew members of the container ship were rescued. According to The Indian Express, the captain of the ship is 62-year-old Russian A. Ivanov; the crew also included 20 Filipinos, 2 Ukrainians and 1 Georgian citizen. The container ship MSC ELSA 3 was operating under the flag of Liberia. The ship was built at the Szczecin Shipyard in Poland in 1997; it is 184 m long and 25.3 m wide and belongs to the Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC). There were 643 containers on board the ship at the time of the incident. 13 of them contained dangerous goods, the details of which are currently unknown, and 12 containers contained calcium carbide. More than 100 containers were lost overboard and are drifting at sea at a speed of 3 km/h. Calcium carbide is a hazardous substance included in the List of dangerous goods of the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods under number 1402. This substance is included in hazard subclass 4.3 ÔÇô Substances that emit flammable gases in contact with water. For this substance, depending on its degree of purity, 2 packing groups have been defined: I (substances with a high degree of danger) and II (substances with a medium degree of danger). Calcium carbide, according to the degree of its health effect, belongs to hazard class 1 (extremely hazardous substances) according to GOST 12.1.007 "Harmful substances". Calcium carbide dust has an irritating effect on the skin, mucous membranes of the respiratory system and eyes. Calcium carbide decomposes when exposed to water, releasing acetylene and calcium hydroxide. The reaction proceeds with the release of heat, and acetylene is also released when in contact with oxidizers. It is reported that the ship's fuel tanks contained 84.44 tons of diesel fuel and 367.1 tons of fuel oil. The state government warned that the oil slick could spread along the entire coast of the region and issued a corresponding warning. The incident with the container ship MSC ELSA 3 has joined the list of major maritime emergencies, the previous of which took place in the Iranian port of Shahid Rajaee on April 26, 2025, and comments on which we published on our website on May 12. In this light, the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association's seminar on Technical Regulation in the Field of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods by Sea, in Seaports and Terminals" to be held on June 17 is particularly relevant. The seminar will discuss the most important issues related to ensuring the safety of the sea transportation of dangerous goods and analyze the causes of major incidents in sea transport and seaports, including recent incidents. | |
Technical regulation in the field of transportation of dangerous goods by sea transport, in sea ports and terminals | 12.05.2025 |

On June 17, 2025, at the address: St. Petersburg, Ulitsa Marshala Govorova Street, 35A, Business Center "Zheolty Ugol", audience ´┐Ż 120, a seminar will be held on issues of technical regulation when working with dangerous goods in maritime transport and at maritime transport infrastructure facilities. On the agenda:
Representatives of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation, Rostransnadzor, Rostekhnadzor, Rosprirodnadzor, representatives of business, scientific organizations and Russian classification societies are invited to the seminar. Participation is free for representatives of government agencies and state scientific institutions, without a registration fee, after filling out an application. During the seminar, participants are provided with free lunches and coffee breaks. | |
UN expresses concern about ensuring safety in handling hazardous chemicals | 12.05.2025 |
  
The massive explosion at the Iranian port of Shahid Rajaei near Bandar Abbas on 26 April 2025, killing at least 57 people and which the Iranian government claims was caused by negligence and poor safety measures in storing and handling hazardous chemicals, has prompted a serious response from UN experts, as reported on the website of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) on 9 May. To prevent and mitigate the impact of potential similar incidents, Member States around the world are invited to participate in the ongoing inter-agency work of UNECE to support governments in strengthening safety and security measures in all sectors involved in handling hazardous chemicals. Experts point out that major explosions at ports in Lebanon (Port of Beirut in 2020) and China (Port of Tianjin in 2015), as well as explosions in Equatorial Guinea (Bata Barracks in 2021) and the United States (West Fertilizer explosion in 2013) were caused by improper storage and handling of hazardous chemicals. These events have prompted governments to step up inspections of chemical plants, review chemical stockpile management, strengthen compliance monitoring, and identify suspected violations. As governments review and improve safety measures, risks need to be carefully assessed against the backdrop of the ongoing global energy transition to mitigate climate change and adapt to its growing impact. Some hazardous substances and technologies associated with the energy transition could lead to accidents if not managed properly. In a changing climate, increasingly severe and frequent natural disasters can cause accidents and worsen their impacts. International guidance and standards help governments manage the risks posed by hazardous chemicals to prevent, prepare for and respond to industrial accidents. An important part of this process is the UNECE Convention on the Transboundary Effects of Industrial Accidents, signed in Helsinki, Finland, on 17 March 1992 and which entered into force on 19 April 2000. This document provides principles and guidance on risk management for industrial disasters aimed at improving industrial safety at the national and transboundary levels. At the UN level, the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals and the UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods set out measures for the safe storage, handling and transport of hazardous chemicals. The International Labor Organization (ILO), the International Maritime Organization (IMO), the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR), the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the UNEP/OCHA Joint Environment Unit, the United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR), the World Health Organization (WHO), the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), the European Commission and the European Investment Bank also support risk management from different perspectives, using relevant legal and policy instruments and guidance. UNECE also initiated a partnership with these organizations to conduct an analysis of the consequences of the 2020 Beirut port explosion and implement a three-year global project supported by the European Union and the European Investment Bank. The initiative aims to promote and raise awareness of international instruments that are used throughout the life cycle of chemicals to prevent and mitigate the consequences of accidents, strengthen the capacity to develop appropriate policies and management, and raise awareness of authorities at different levels of preparedness and response. International cooperation and coordination, including between relevant sectors, are key factors in expanding knowledge and developing tools to avoid future incidents with hazardous chemicals and protect people, the environment and the economy from them. According to experts from the IDGCA NP, the most important aspect is, of course, the correct application of international conventions, codes, agreements, rules and guidelines to coastal infrastructure facilities and their adaptation to national legislation. Sometimes hasty references to international documents, which do not always have an official translation into the national language, can lead to negative consequences for safety and to a decrease in attention to the national regulatory framework, taking into account the specifics of each state. Particular attention should be paid to the professional training of specialists at all levels in the field of transportation of dangerous goods and cargo operations with dangerous goods. Thus, for reasons unknown to many, the current regulation on licensing of loading and unloading activities in relation to dangerous goods on inland water transport, in seaports, approved by RF Government Resolution ´┐Ż 2111 dated November 30, 2021, has eliminated requirements for special training of persons responsible for working with dangerous goods. | |
Happy Victory Day | 07.05.2025 |
 The International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association deeply honors the memory of those who, giving their all, defended the Motherland and the world from the brown plague during the Great Patriotic War. These days, on the eve of the celebration of the eightieth anniversary of the victory over Nazi Germany, many of us look at photographs of our loved ones who went through the war and defeated the enemy, and pay tribute to their memory by laying flowers on the graves of the heroes. We sincerely congratulate everyone on the holiday, wishing you health and prosperity! Sincerely yours, President of the International Association, Moshkov G.Yu., and General Director of the International Association, Ognev M.I. | |
Upcoming training courses for specialists in the transportation of dangerous goods | 30.04.2025 |
 
From May 19 to 23, 2025, the International Staff Training Center at the address St. Petersburg, ulitsa Marshala Govorova Street, bld. 35A, office 120 will host in-person training for specialists whose activities are related to the transportation, handling and classification of dangerous goods. The classes will be based on the study of international Rules, Conventions, Codes concerning the transportation of dangerous goods and national regulations, including the draft of the new Technical Regulations on the safety of maritime transport facilities and maritime transport infrastructure, as well as the draft amendments to the Merchant Shipping Code concerning the requirements for working with dangerous goods at sea terminals. Practical classes during the training period will examine known emergency situations involving dangerous goods, their causes and methods for preventing accidents. The purpose of the training is to acquire risk management skills when working with dangerous goods. Based on the results of training and examinations, State-issued Certificates and Certificates of Attestation on behalf of the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association will be issued. Classes can also be held remotely. | |
Explosion in Iranian port | 30.04.2025 |
 
In the Iranian port of Shahid-Rajai, located 23 km from the city of Bandar Abbas on the coast of the Strait of Hormuz, a massive explosion occurred on April 26, killing more than 40 people. This brings to mind the large-scale tragedy that erupted on the evening of August 4, 2020, in the port of Beirut, where two ammonium nitrate explosions occurred at once. The power of one of the explosions was estimated at 1.2 kilotons of TNT, only 10 times weaker than the power of the first ever atomic bomb, "Little Boy", which was dropped on Hiroshima, Japan, in August 1945, almost exactly 75 years before the tragedy in the Lebanese capital. As a result of the man-made disaster, more than 170 people died, 6 thousand were injured, and 300 thousand Beirut residents lost their homes. Apparently, as often happens in emergencies of this scale, the Beirut incident was caused by a chain of factors, the main one of which can be called blatant human negligence. Ammonium nitrate is an ammonium salt of nitric acid and has the chemical formula NH4NO3 and consists of three chemical elements nitrogen, hydrogen and oxygen. The high nitrogen content (about a third by weight) in a form easily assimilated by plants allows ammonium nitrate to be widely used as an effective nitrogen fertilizer in agriculture. In this capacity, ammonium nitrate is used both in pure form and as part of other, complex fertilizers. The bulk of the nitrate produced in the world is used precisely in this capacity. Physically, ammonium nitrate is a white crystalline substance, which in industrial form has the form of granules of various sizes. It is hygroscopic, that is, it absorbs moisture from the atmosphere well; during storage, it tends to cake, forming large dense masses. Therefore, it is stored and transported not as a solid bulk mass, but in dense and strong bags that do not allow the formation of large compacted masses that are difficult to loosen. Ammonium nitrate is included in many types of industrial explosives and is widely used as such, mainly in the mining industry. Quite a few parallels can be drawn between the events in Beirut and Shahid Rajaee. The blast at the port of Shahid Rajaee on April 26, 2025, produced such a strong shock wave that its impact was felt within a radius of 50 km. Port infrastructure and nearby buildings were literally wiped off the map, and windows were blown out in homes across the city and surrounding areas. What caused the explosion? CNN previously reported that hundreds of tons of chemicals arrived at the port in February, with a second shipment arriving in March. The state-run Islamic Republic News Agency reported late Saturday that Iran's Customs Administration attributed the incident to the presence of hazardous cargo and chemical materials at the port. Iran's National Oil Company said the blast at the port was not related to refineries, fuel tanks or pipelines in the area. Iranian officials have denied that any military-usable materials were stored at the port. Ebrahim Rezaei, a spokesman for the Iranian parliament's National Security and Foreign Policy Committee, said in a statement on Sunday that initial reports indicated the blast "had no connection to Iran's defense sector." Iranian President Masoud Pezeshkian arrived in Bandar Abbas on Sunday afternoon to investigate the situation and oversee relief efforts, state media reported. The president also met with victims of yesterday's blast. The blast comes at a time of high tension in the Middle East and ongoing talks between Iran and the United States over Tehran's nuclear program. Tehran has denied that it was a terrorist attack and has denied that Israel was involved. Some speculation about the specific chemicals that has appeared in some Western media outlets is not entirely certain ÔÇô for example, reports that the material that exploded was sodium perchlorate, described as "the main component of solid rocket fuel," which is incorrect since the substance is not itself a component of rocket fuel, but is used in the production of ammonium perchlorate, which is, in fact, used in solid rocket fuels. Sodium perchlorate NaClO4 is a sodium salt of perchloric acid, which is a strong oxidizer. When crystallizing from aqueous solutions at temperatures above 51°C, the anhydrous salt precipitates, below 51°C monohydrate NaClO4H2O, below -13 degrees ÔÇô dehydrate. Both the anhydrous salt and the crystal hydrates are very hygroscopic, so sodium perchlorate is mainly used as a raw material for obtaining other perchlorates in exchange reactions. Some media outlets suggest that ammonium nitrate exploded, but there is no confirmation of this either. Although it is too early to draw any reasonable conclusions about the causes of the tragedy, the issue of ÔÇťhuman factorÔÇŁ traditionally comes to the forefront, when we see that port employees did not have sufficient qualifications to ensure the proper level of safety when handling and storing dangerous goods in containers. And this is confirmed by the Tasnim agencyÔÇÖs report that, according to Iranian Interior Minister Eskander Moameni, the explosion at the Shahid Rajaee commercial port in the city of Bandar Abbas was caused by negligence, and the culprits have already been found. | |
Loading master of LNG terminal | 11.04.2025 |
 
The training and certification of specialists for work at LNG terminals has been successfully completed at the ISTC. The educational plan and training program reflected the requirements of national and international documents, as well as presented the practice of safe work at LNG terminals and gas tankers, and are unique, since they were prepared taking into account the job responsibilities of the students. Among the teachers, there is one doctor and three candidates of technical sciences, as well as highly qualified experts in the field of cryogenic engineering and navigation safety, including a deep-sea captain who has worked on tankers for many years. The results of the certification showed that all trainees meet the established competencies for a loading master of LNG terminal. Training of specialists ensuring interaction between vessel and terminal and working with oil products, gases and chemicals is a priority at the ISTC as the most complex and necessary task for Russian companies. The Russian Federation is actively expanding its capacity for the production of refrigerated liquefied gases, including cryogenic, and develops relevant standards and regulatory documents. It is especially important when new regulatory documents take into account not only the interests of administrative and certification bodies, but also the interests of all companies involved in design, production, transporting and processing. We would also like the initiators and developers of regulatory legal acts in the field of navigation safety, regulation of the activities of maritime transport infrastructure facilities, which include LNG marine terminals, to take into account the mandatory nature of personnel training, since, as we can see, new regulatory documents do not contain requirements for mandatory personnel training, although such requirements were previously present. The work of a loading master of LNG terminal is extremely responsible and requires from a specialist not only good knowledge, technical training, but also high erudition. The ISTC believes that this task was completed when preparing the given group of students. | |
Chartering ships involves risks | 14.03.2025 |
 
Chartering ships is an integral part of the maritime business and is often the subject of litigation between the ship owner and the charterer. To prepare chartering agreements, it is necessary that the people responsible for preparing the agreements have a broad erudition, have undergone the necessary professional training and have extensive knowledge in areas related to both the commercial component of chartering and the safety of navigation. Participants in disputes arising between a ship owner and a charterer may be lawyers, insurance companies, port authorities, creditors, leasing companies and many others. In the modern geopolitical situation, chartering is becoming an even more serious transaction between the parties, taking into account the class and flag of the vessel, the region of navigation, and ports of call. In cases where litigation occurs, expert, surveyor companies, classification societies are involved in resolving disputes. Currently, the independent survey company Russian Register Ltd., which is a 100% subsidiary of the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (IDGCA NP), has been appointed by the court as an expert organization. The court also recognized and authorized the company's experts to conduct an examination by answering the court's questions. As a rule, experts are appointed specialists who have many years of practice, experience in the field in which the disputes arose, and who do not have any dependence on either party to the dispute. In this case, the experts in the case were captain of the deep-sea voyage Vladimir Dmitrievich Dmitrievsky, who has many years of experience as a captain of the deep-sea voyage, including in the northern latitudes, Vladimir Vasilyevich Gadalov, who has many years of experience in the shipbuilding industry and in the classification society, and Mikhail Ivanovich Ognev, who has many years of experience in the northern and southern latitudes as a chief engineer, and many years of experience in the classification society, as well as extensive experience in conducting various examinations and developing expert assessments. On March 13, 2025, the next meeting of the expert group was held. 
As practice has shown, when conducting various investigations and examinations, the risk of disputes is laid at the stage of concluding contracts, planning voyages and preparing for the fulfillment of the terms of the contract by both parties. It is for these purposes that serious professional training is required for all participants in ship chartering transactions. The International Staff Training Center, which is a 100% subsidiary of IDGCA NP, conducts unique training courses for ship chartering specialists. Last year, specialists and heads of departments of the Sakhalin Energy company underwent training. A series of courses on ship chartering are also planned for the current year. The peculiarity of the development of training programs in this area is taking into account the specifics of the companies' activities and the job responsibilities of the persons who plan to undergo training. The next courses are planned from 19 to 23 May 2025, however, the courses can also be held as groups are formed (at least 5 people). Experts involved in conducting forensic examinations, in particular, those mentioned above, also participate in the training and teach methods and practices that help reduce the risks of conflicts. | |
Collision between ships carrying dangerous goods | 11.03.2025 |
 
On 10 March, the Portuguese-flagged container ship Solong collided with the US-flagged tanker Stena Immaculate, owned by Stena Bulk, at anchor. Solong left Grangemouth, near Edinburgh, on 9 March, heading up the UK east coast to Rotterdam. The tanker arrived at Immingham anchorage on 9 March. At the time of the collision, the tanker was carrying approximately 220,000 barrels of aviation fuel (believed to be FUEL, AVIATION, TURBINE ENGINE, UN 1863, Hazard Class 3, Flammable Liquids, in the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code list of dangerous goods). The container ship was carrying an unknown quantity of alcohol and 15 containers of sodium cyanide. Both vessels were significantly damaged, and one crew member of the container ship is still missing. The tanker crew abandoned ship after several explosions on board, and there were no casualties among the crew. Of particular concern is the presence of sodium cyanide on board the container ship. Sodium cyanide is represented in the list of dangerous goods of the IMDG Code by two items: SODIUM CYANIDE, SOLID, hazard division 6.1 (toxic substances), UN Ôäľ 1689, and SODIUM CYANIDE SOLUTION, hazard division 6.1, UN Ôäľ 3414. As far as can be judged from the available information, SODIUM CYANIDE, SOLID, was on board the container ship. SODIUM CYANIDE, SOLID, is a packing group I (high danger substances) and is a marine pollutant. Carriage in containers is carried out in accordance with instruction P002 with special provision PP31 (packaging must be hermetically sealed), in intermediate bulk containers (IBC) in accordance with instruction IBC07 with special provision B1 (the cargo must be carried in closed cargo transport units or cargo containers/vehicles, which must be equipped with rigid sides or fences of a height at least equal to the height of the IBC). In addition, this substance may be carried in portable tanks in accordance with instruction T6 with special provision TP33. Cargo stowage category on board is B category (depending on the characteristics of the vessel, either only on deck or both on deck and under deck), segregation code SG35 (stowage separately from acids). SODIUM CYANIDE SOLID, according to the provisions of section 1.4.3 of Provisions for High-Danger Cargoes of the IMDG Code, is a high danger cargo (cargo that can be used for terrorist purposes). After a detailed investigation of this incident, there will undoubtedly be a tightening of the rules for the movement and mooring of ships in the waters of sea ports. The International Association of Classification Societies (IACS), which often acts as the initiator of IMO circulars in terms of strengthening safety measures at sea, will certainly respond to this event. | |
Training of specialists in dangerous goods | 19.02.2025 |
  
Experts from the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association and specialists from its subsidiary, the International Staff Training Center (ISTC), at the request of companies working with dangerous goods, develop recommendations on which specialists in the field of dangerous goods and which training programs should be trained, based on the company's activity profile and the job responsibilities of its employees. What risks may a company that carries out work with dangerous goods face if it does not have specialists trained in handling these goods on its staff? This is determined by the physicochemical, toxicological and other potential negative factors inherent in these goods, their state of aggregation, the state of their restraint means, and the method of transportation and handling. First of all, this is the risk of explosion and fire, which is very clearly demonstrated by the tragedy that occurred in Beirut on August 4, 2020. Many dangerous goods and / or their combustion products are toxic and corrosive. However, there are also economic risks. For example, dangerous goods that are incorrectly stowed, or have markings that are not provided for by the transportation rules, or are incorrectly documented in the transport document may cause the ship to be detained in a foreign port, which causes huge financial costs for the company that made such mistakes. To avoid these mistakes, each company that handles dangerous goods must have properly trained personnel.Employees of companies that transport and handle high-consequence goods - goods that can be used for terrorist purposes - must undergo special training. The dangerous goods handled at the enterprises are both packaged and liquid and bulk. Thus, special training should be undergone by the employees of sea and river terminals, employees of stevedoring companies, employees of motor transport enterprises (drivers, forwarders, dispatchers), employees of railway infrastructure (engine drivers, switching crew employees, wagon inspectors, dispatchers, station attendants), employees of airlines and other employees of the transport industry, consignors and consignees. Such training is necessary for the employees of testing laboratories that classify dangerous goods, manufacturers of containers for dangerous goods and high-capacity containers, including specialized ones, including tank containers, manufacturers of equipment for loading and unloading operations, including standpipes and manifolds for working with liquid cargoes, including aggressive liquids and cryogenic products. The officials of seaport administrations, employees of supervisory, customs and other government agencies that supervise and control the turnover of dangerous goods should also be trained in handling dangerous goods. Dangerous goods are used in various fields of technology, science and medicine and require special treatment everywhere.Thus, personnel operating an oxygen converter in a medical institution, without proper training, may perform incorrect actions, as a result of which oxygen may enter into, for example, a dangerous reaction with organic substances, which is fraught with the occurrence of an explosion and/or fire. To help site visitors determine whether they are dealing with dangerous goods and, accordingly, whether they are required to undergo specialized training, we will give a definition of dangerous goods. According to GOST R 57478-2017 "Dangerous goods - Classification´┐Ż dangerous goods are substances (mixtures of substances, solutions), materials, products or wastes from production or other activities that meet classification indicators, criteria or characteristics and, due to their inherent properties and in the presence of certain factors, can cause damage to the environment, material damage, death, injury, poisoning, illness of people and animals. Training of specialists in the transportation and handling of dangerous goods on all types of transport has been conducting at the ISTC since 2003. Depending on the level of initial training of candidates for training and their job responsibilities, the volume of the professional development program ranges from 16 academic hours to 80 academic hours and, if necessary, more. The ISTC has basic professional development courses for specialists in the field of dangerous goods for sea and inland water transport, rail transport, road and air transport. Depending on the needs of enterprises sending their employees to the ISTC, exclusive programs are developed on the basis of these programs, taking into account their job responsibilities. Students who successfully pass the final exams are presented for certification by the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association, and in addition to certificates of professional development, they are awarded international certificates.     | |
Hydrogen - the fuel of the future | 14.02.2025 |
 
It is known that hydrogen has a special place among alternative energy sources, therefore energy specialists are very interested in news regarding the commissioning of hydrogen production plants and the expansion of their capacities. There are several known methods for industrial hydrogen production, which include steam converting (reforming) of methane (natural gas), coal gasification, water electrolysis, pyrolysis, biotechnology, etc. Many of these technologies do not meet modern environmental safety requirements. The most environmentally friendly is water electrolysis in alkaline-type electrolyzers. However, this method is quite energy-intensive. A test bench complex was launched at the Kola Nuclear Power Station, which will produce up to 150 tons of hydrogen per year. The test complex at the Kola NPS is a pilot site for hydrogen production using a new technology, in which electrolyzers with proton exchange membranes are used instead of alkaline-type electrolyzers, providing higher energy efficiency of the plant due to the absence of a liquid electrolyte. In such an electrolyzer, water electrolysis occurs in a cell equipped with a solid polymer electrolyte that conducts protons, separates the reaction products and provides electrical insulation of the device's electrodes. The purity of the hydrogen produced in such an electrolyzer is 99.999%. Hydrogen is presented for transportation and is transported in two states: cooled liquid, UN ? 1966, and compressed, UN ? 1049; the hazard subclass of this substance is 2.1 - flammable gases. Cooled liquid hydrogen can be transported both in containers, which are so-called Dewar vessels, and in portable tanks intended for transportation by all types of transport. When transporting this substance, its special thermophysical properties should be taken into account. Thus, the boiling point at normal atmospheric pressure is -252.7´┐ŻC, which requires equipping the equipment for transporting liquid hydrogen with highly efficient, and therefore expensive, cryogenic thermal insulation. At the same time, the density of liquid hydrogen is extremely low and is 70.8 kg/m3 It should be added that, despite the technological difficulties, the world has already accumulated quite a lot of experience in the construction and operation of tankers for transporting liquid hydrogen. The transportation and storage of liquid hydrogen, due to its special thermophysical properties and the high probability of fire and explosion risks, require very serious professional training of all personnel involved in the design, production and operation of transport equipment and transport containers intended for the transportation of liquid hydrogen. The International Staff Training Center conducts such training as training groups are formed. 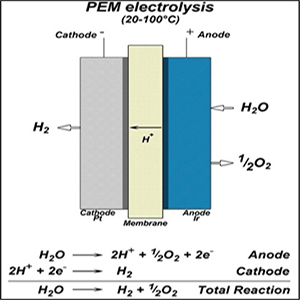  | |
Outcomes of the 65th session of the UN ECOSOC Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods | 06.02.2025 |

The official report on the outcome of the 65th session of the UN ECOSOC Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, held at the Palais des Nations (Geneva) from 25 November to 3 December 2024, has been published. This document contains the following information. First of all, the report notes that the experts reviewed the recommendations developed by the Sub-Committee at its sixty-second, sixty-third and sixty-fourth sessions and noted the outstanding issues related to their implementation. The report pays much attention to explosives and related issues, in particular, clarifies the requirements for two series of explosives tests, provisions related to "UN standard detonators", provides a review of the requirements for the packaging and transportation of ammonium nitrate emulsions, and considers the impact of the use of electric power sources and alternative fuels on the safety of the transport of explosives. Many issues were considered under the agenda item of the session "Listing, classification and packaging". In particular, a new definition of a single packaging was developed, new aspects related to airbags, the carriage of organic hydrogen compounds, used medical equipment containing lithium batteries were considered, and amendments concerning a number of specific dangerous goods were approved. Special discussions were held on issues related to power sources based on lithium batteries and sodium-ion batteries. Significant attention in the report was paid to the transportation of gases, in particular, to the worldwide recognition of UN and non-UN pressure vessels. In this regard, it should be noted that the Subcommittee experts assessed the proposal of the Russian Federation to develop a new section of the UN Model Regulations 6.9.4 "Requirements for the design, construction, inspection and testing of portable tanks with fiber-reinforced plastics (FPR) shells intended for the carriage of non-refrigerated liquefied gases". Some experts supported the intention to establish an informal working group to work further on this proposal, while others were in favor of first obtaining confirmation of the safety concept of such portable tanks before establishing an informal working group. The Russian expert proposed testing a virtual prototype to confirm the safety concept. He expressed his intention to submit an official document on this issue at the next session. The Russian expert invited all interested parties to join an intersessional correspondence group on this issue. The Subcommittee agreed to consider this issue in detail during the next biennium. The document addresses issues related to the global harmonization of dangerous goods regulations with the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, the Guidelines of the Model Regulations, unified interpretations of the Model Regulations and their implementation. The report also includes issues related to the Subcommittee's cooperation with the International Atomic Energy Agency. The document devotes considerable attention to the issue of training on the safety of the transport of dangerous goods. It also touches upon a number of issues related to the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. In addition, the document contains provisions related to the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the Subcommittee's work programme for the 2025-2026 biennium, and the application of ISO standards. It is important to note that when considering various proposals to amend the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, the Subcommittee welcomed the amendments to the Russian version of the Model Regulations made by the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association and asked the secretariat to take into account the proposed changes in the upcoming revised edition (paragraph 86 of the report). These amendments were presented by M.I. Ognev, the Director General of IDGCA NP, who participated in the session. A total of 55 working and 65 information documents were considered during the session. The main result of this work was the approval of amendments and changes that will be introduced into almost all parts of the successive editions of the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods and the UN Manual of Tests and Criteria. The next, 66th session of the Subcommittee will be held from 30 June to 4 July 2025 in Geneva. The deadline for submitting official documents for consideration at the session is 4 April 2025. There is no deadline for submitting information documents; they can be sent to the secretariat at any time before the session and even during it. The decisions taken at the 65th session of the Subcommittee and the agreed changes to the regulations on the transport of dangerous goods will be taken into account in the content of the training programs of the ISTC.   | |
Ignorance of the rules for transporting oxygen and handling oxygen can lead to an aircraft crash. | 05.02.2025 |
 
As is known from several media reports, recently a light medical aircraft Learjet 55, with 6 people on board, crashed in a residential area of the American city of Philadelphia (Pennsylvania). All crew members and passengers died. Another victim of the crash was the driver of the car, who was closest to the crash site. The preliminary cause of the crash is called the explosion of an oxygen cylinder on board the Learjet 55. Compressed oxygen is a dangerous cargo, which has been assigned UN number 1072, basic hazard division 2.2 (non-flammable non-toxic gases), additional hazard division 5.1 (oxidizing substances). The ICAO Technical Instructions for the Safe Transport of Dangerous Goods by Air (ICAO TI) allow the air transportation of compressed oxygen in cylinders. The maximum net oxygen quantity per package is 75 kg for passenger aircraft and 150 kg for cargo aircraft. When preparing cargo for air transport, Packing Instruction 200 applies, special provision S of which states the following:
At the same time, according to Packing Instruction 200, cylinders must be tested every 10 years. In addition, when transporting compressed oxygen by air, a special provision of the ICAO Technical Instructions A175 applies, which states: Oxygen cylinders intended for emergency use and transported in accordance with this provision may be fitted with cartridges to activate them (cartridges for starting mechanisms, category 1.4, compatibility group C or S) without changing their classification as category (division) 2.2, provided that the total quantity of propellant explosives does not exceed 3.2 g per oxygen cylinder. Cylinders fitted with cartridges to activate them and prepared for transport must be provided with effective means to prevent accidental activation. As can be seen, despite the fundamental permission of the ICAO Technical Instructions for the Safe Transport of Dangerous Goods by Air to transport compressed oxygen by air, any deviation from the rules and instructions prescribed by this document can lead to catastrophic consequences. | |
Liquid ammonia paves the way through the port of Ust-Luga | 04.02.2025 |
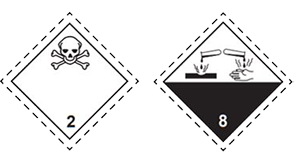
In December 2024, the first stage of the ammonia transshipment terminal was launched at the Port Favor terminal in Ust-Luga (Leningrad Region). Only about 5 years passed from the signing of the memorandum on the realization of this project at the St. Petersburg International Economic Forum in 2019 until the commissioning of the first stage of the terminal. Ammonia is a dangerous goods (UN number 1005, main hazard division 2.3 (toxic gases), additional hazard class 8 (corrosive substances)) and, in accordance with the international codes and regulations for the transport of dangerous goods (IMDG, ADN, ADR, Appendix 2 to SMGS) and the RF Government Resolution dated March 10, 2022 ? 341 "On approval of the list of types of high-consequence goods", refers to to high-consequence goods (goods that can be used for terrorist purposes). Due to this, in order to ensure the legal basis for the construction of marine ammonia terminals, amendments were made to the Water Code of the Russian Federation by Federal Law dated December 19, 2023 ? 613-FZ "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation". In accordance with these amendments, subparagraph 2) of paragraph 15 of Article 65 of the Federal Law dated June 03, 2006 ? 74 "Water Code of the Russian Federation", which defines prohibitions on certain types of activities within the boundaries of water protection zones, excluded the imposition of a ban on the placement of specialized storage facilities for ammonia, methanol, ammonium nitrate and potassium nitrate in water protection zones on the territories of seaports, the list of which is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation, outside the boundaries of coastal protection belts. In accordance with the definition of paragraph 11 of Article 65 of the Water Code of the Russian Federation, the width of the coastal protection belt is established depending on the slope of the shore of the water body and is thirty meters for a reverse or zero slope, forty meters for a slope of up to three degrees and fifty meters for a slope of three degrees or more. As part of the first stage of the terminal construction, overpasses for unloading from tank trucks were erected, a nitrogen unit was installed, a central control panel, a process pipeline, a loading unit at the berth for loading onto a vessel were equipped, power supply, water supply, sewerage, fire extinguishing networks were laid, and a flare unit was built. As part of the second stage, a process line for transshipment of the product from railway tank cars will be built. The first process line eliminates the risk of spills of liquid ammonia and emissions of its vapors, it is equipped with a modern automatic control system. Today, the daily capacity of the terminal is 2.6 thousand tons of cargo. At the same time, liquid ammonia is delivered to the terminal in tank trucks, and from May 2025, rail transport will be used for this purpose, which will increase the daily capacity by one and a half times. From 2026, up to 1.5 million tons of ammonia will be transshipped through Ust-Luga annually. The start of ammonia transshipment in Ust-Luga opens up opportunities for restoring production capacities and completing investment projects aimed at increasing ammonia production volumes, which means that world markets, primarily the markets of friendly countries, will be open to its supplies. Ammonia has found wide application in industry, primarily for the production of ammonia and ammonium nitrate fertilizers (ammonium nitrate and nitrate, ammonium chloride, ammonium sulfate and others), in the production of nitric acid, for the production of ammonites - ammonia explosives, ammonia is used as a solvent for various inorganic and organic substances, as a coolant, and also as an oxidizer for rocket fuel. Ammonia is attracting increasing attention as an alternative marine fuel. The latter issue was considered in 2023 and 2024 at two International Conferences "Multimodal Transport of Dangerous Goods. Fuel of the Future - the Path to Sustainable Development", successfully held by the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (IDGCA NP). Preparations are currently underway for the next conference, the dates of which are being specified. In light of the growing interest in ammonia, experts from the IDGCA NP, together with instructors from the International Staff Training Center (ISTC), have prepared training programs to improve the qualifications of personnel involved in the handling, storage, and transportation of ammonia. These programs have been developed taking into account the requirement that all employees of companies involved in the transportation, handling, and storage of high-consequence goods must undergo mandatory special training. In this regard, we invite owners of marine chemical terminals and companies operating on the territory of chemical terminals to send their specialists for training at the ISTC in the following advanced training programs:
The programs are designed for employees of various categories: managers, engineering and technical personnel, and rank-and-file personnel.
A written exam and an interview are held upon completion of the training. Students who successfully pass the exam are awarded a certificate of advanced training and an international certificate.    | |
Results of the 11th session of the IMO Sub-Committee on Ship Design and Construction | 03.02.2025 |

The 11th session of the Sub-Committee on Ship Design and Construction (SDC) was held from 13 to 17 January in London at the headquarters of the International Maritime Organization. The Russian delegation took part in the event. Ships Other Than Tankers, and also prepared amendments to the new version of the Revised Guidelines for Ships' Towing and Mooring Equipment (resolution MSC.1/Circ.1175/Rev.2). The Sub-Committee also agreed on Amendments to Regulation 25.3 (Safety of Crew) of the Load Lines Convention 1966, which contain, inter alia, additions on the need to install guard rails around all openings and wells to which the crew is expected to have access. The above documents and amendments will be submitted for approval to the 110th session of the Maritime Safety Committee (MSC 110) and for adoption at MSC 111 with an effective date from January 1, 2028. During the session, further development of the International Code for the Carriage of Industrial Personnel (IP Code) and related guidelines was continued. In particular, the Sub-Committee prepared and agreed on draft amendments to Part IV of the IP Code concerning the inclusion of the weight of industrial personnel (90 kg) in stability calculations for cargo ships certified in accordance with Chapter I of SOLAS and carrying industrial personnel. Similar stability calculation requirements already exist in Part V of the IP Code for high-speed craft. The amendments will apply to new ships taking into account the date of the contract for the construction of the ship, which will be determined when the amendments are adopted at MSC 110. The Sub-Committee considered and adopted amendments to the International Code on the Enhanced Programme of Inspections during Surveys of Bulk Carriers and Oil Tankers (ESP Code) concerning the use of remote inspection tools (RIT) for the survey of hull structures of bulk carriers and oil tankers. The amendments include key provisions and requirements for the application of RIT, as well as the procedure for the certification of enterprises performing close-up inspection of hull structures using RIT. The planned entry into force of the amendments is January 1, 2028. Another area of work of the Sub-Committee was the preparation and agreement of amendments to the Code of Alerts and Indicators, 2009, which are planned for adoption at the 34th IMO Assembly in December 2025. The amendments take into account the requirements of new IMO instruments that have entered into force since the adoption of the Code 2009, including the International Code of Safety for Ships using Gases or other Low-flashpoint Fuels, the International Code for Safety of Ships Carrying Industrial Personnel, the International Ship and Port Facility Security Code, the Code for Approval of Ballast Water Management Systems and others. The Code of Alerts and Indicators, although a non-mandatory IMO instrument, is highly sought after by the industry, providing consolidated references to ship alerts and signals provided for in other Conventions and Codes, including information on their prioritization, grouping, aggregation, location and type, including colour and symbols. The Sub-Committee continued its consideration of issues related to the reduction of underwater noise from commercial shipping, including key aspects of the IMO Action Plan to Reduce Underwater Noise. As part of the experience accumulation phase on underwater noise reduction, the session discussed a system for monitoring the effectiveness of existing energy efficiency measures on ships to reduce underwater noise, as well as potential future research to improve the understanding and assessment of underwater noise levels emitted by ships. A number of other issues were considered, including revisions to the Explanatory Notes on the assessment of the performance of ship systems on passenger ships following incidents involving fire or flooding, with a view to the safe return of the ship to port (MSC.1/Circ.1369); issues of increasing the use of reinforced plastics in ship hull structures; and unified interpretations of the requirements of international Conventions and other IMO instruments. The next session of the Sub-Committee (SDC 12) will be held from 19 to 23 January 2026. +Source: Official website of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation | |
IDGCA partner, NBE Ltd., has expanded the scope of its safety activities | 22.01.2025 |
|
A full member of the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association, National Bureau of Expertise Ltd. (hereinafter - NBE Ltd.), has expanded the list of services performed within the framework of licensed activities for the installation, maintenance and repair of fire safety equipment for buildings and facilities. The license allows performing the following types of work. NBE Ltd. has been operating since 1999 and provides a wide range of services in various industries. NBE Ltd took part in major oil-and-gas projects: on the development of offshore oil-and-gas fields named after V. Filanovsky and Yu. Korchagin in the northern part of the Caspian Sea, on the construction of the Yamal LNG and Arctic LNG 2 plants and many others. When carrying out work, NBE Ltd. closely cooperates with research centers and scientists. Knowledge of international standards and practices allows NBE Ltd. to participate in major international projects, which include Yamal LNG and Arctic LNG 2. Having an updated EMERCOM license will facilitate further promotion of NBE Ltd. services. | |
UNECE develops solutions to reduce the carbon footprint of road transport of dangerous goods | 21.01.2025 |
 
UNECE experts have developed new technical solutions for the use of electric vehicles for the transport of dangerous goods, which have only recently come into use for this purpose (it is known that one of the first electric vehicles for the transport of dangerous goods was introduced in the Netherlands in 2017 and was used to transport petrol and diesel fuel). In 2023, the UNECE Working Group on the Transport of Dangerous Goods (WP.15) amended the Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) to allow for the first time the use of electric vehicles of AT category (intended for the transport of dangerous goods in various types of tanks or multiple-element gas containers) for the transport of non-flammable dangerous goods. The 2025 edition of ADR, which entered into force on 1 January 2025, now also contains new expanded provisions that allow the use of battery-electric vehicles of FL category (intended for the transport of flammable gases and liquids). In addition, these new provisions allow the use of hydrogen-powered vehicles of AT and FL categories for the transport of dangerous goods. The experts also considered alternative sources of electrical energy such as hydrogen fuel cells. Today, hydrogen is increasingly seen in the transportation industry as a viable alternative to fossil fuels, critical to achieving zero-emission transportation. The new UNECE decisions will ensure the safe use of hydrogen-powered vehicles for the transport of dangerous goods (except explosives). In addition, these decisions also contribute to the transition to green energy in the transport sector by promoting the development of infrastructure, especially for charging electric vehicles and hydrogen refueling. The UNECE Working Group on the Transport of Dangerous Goods is currently exploring the possibility of allowing the transport of explosives on electric and hydrogen-fuelled vehicles. | |
Handling dangerous goods in sea and river ports | 15.01.2025 |
 
Sea and river ports are usually high-risk facilities where large quantities of dangerous goods are transported and stored, and where they are prepared for transportation by sea and river transport. The safety of life and health of crew members and the safety of the environment depend on how the cargo is prepared for transportation, taking into account its compatibility and placement on vessel. Recent accidents, both abroad and in Russia, show that accidents are often caused by the lack of sufficient training of both crews and shore personnel working in sea and river ports. Despite the many international and national regulations and harmonized recommendations, their correct application is a major problem for both ship crew members and shore personnel. That is why the training program for personnel participating in transportation and handling of dangerous goods must take into account the specifics of a particular port, terminal and vessel. Training must be carried out in relation to those facilities where the personnel who want to get such training work. The professional development program "Loading and unloading activities related to dangerous goods in seaports and inland water transport" is most in demand among employees of sea and river ports. Training under this program also allows the graduates to pass certification for Dangerous Goods Safety Advisor and receive an international certificate from the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association. In connection with the above, we inform you that from January 27 to January 31, 2025, the International Staff Training Center (ISTC) will hold training courses for specialists in loading and unloading activities related to dangerous goods in seaports and inland water transport and Dangerous Goods Safety Advisors. The program includes such additional issues as cargo operations for liquid bulk cargoes (oil products, LNG and LHG), bunkering operations in sea and river ports, intra-port transportation of dangerous goods by road and rail, safe transportation and handling of high-consequence dangerous goods (cargoes that can be used for terrorist purposes). The training sessions will be held in a combined format (simultaneously both in the classroom and in real-time webinar mode). We invite managers and specialists of stevedoring and shipping companies, as well as all organizations whose activities are related to the transportation and handling of dangerous goods, to the training. | |
Merry Christmas and Happy New Year | |
 | |
Loading and unloading activities related to dangerous goods on inland waterway transport, in seaports | 14.11.2024 |
 
The International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code (IMDG Code) and other international documents regulating the transportation and handling of dangerous goods, ratified by the Government of the Russian Federation, require mandatory special training for employees whose activities are related to dangerous goods. In accordance with the requirements of Chapter 1.3 of the IMDG Code, regardless of what such a specialist does (marking, loading and unloading, presentation for transportation and acceptance of dangerous goods, development of cargo operation plans, etc.), he must regularly undergo advanced training in order to have sufficient knowledge and practical skills in working with dangerous goods. It should be noted that sea terminals that handle LNG and oil products are also subject to licensing requirements imposed on enterprises carrying out loading and unloading activities related to dangerous goods. The specialists of these terminals, along with the specialists of other companies that carry out loading and unloading activities with respect to dangerous goods, periodically undergo training at the International Staff Training Center (ISTC), a subsidiary of the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (IDGCA). It is pleasant to note that many specialists undergo training at the ISTC for the second or for the third time. Such graduates of the courses are issued special certificates of the IDGCA NP. Despite the fact that the ISTC has a standard training program developed by the experts of the IDGCA NP, the program of the next courses is adjusted and adapted each time taking into account the specific characteristics of the enterprises and the job responsibilities of the students. The next training of specialists in the field of loading and unloading activities with respect to dangerous goods will be held from November 18 to 22 in a combined (face-to-face and distance) form. The course program includes practical classes using visual aids, including equipment for the transport of dangerous goods. The next courses will be held from December 09 to 13, 2024 | |
Requirements for transportation and storage of fireworks | 28.10.2024 |
On October 27, a fire followed by explosions of fireworks occurred in a pyrotechnics store in the city of Hyderabad in the Indian state of Telangana. The circumstances of the incident are being established. In May 2024, a fire was reported at one of the Indian fireworks factories. Unfortunately, similar incidents with fireworks occur in various countries, and this indicates the need for the most serious attitude to the handling of such dangerous items at all stages of their life cycle, from production to use for their intended purpose. In accordance with the international classification presented in the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods and the industry regulations developed on their basis (IMDG, ADR, ADN, RID Regulation, Annex 2 to SMGS), fireworks are usually classified into hazard divisions 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 and 1.4.
The inclusion of fireworks in hazard subclasses 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 and 1.4 is based on tests of Series 6 of the UN Manual of Tests and Criteria. Fireworks are the subject of special attention of the world expert community. This is evidenced, in particular, by the fact that issues related to improving the rules for their transportation are included in the agendas of almost every session of the UN ECOSOC Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, in which representatives of the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association participate. As for ensuring the safety of storage of fireworks and pyrotechnic products in general, these issues are regulated by legislation in the field of industrial safety. | |
About sulfur again | 28.10.2024 |
  
The official website of OTEKO company, the operator of sea terminals in the port of Taman, published information that a closed sulfur warehouse with a design storage capacity of up to 300 thousand tons has been put into operation. Thanks to this, an increase in sulfur exports through the port of Taman is expected, while the design transshipment volume is 5 million tons per year. The closed sulfur warehouse is the largest in the world; its area is 2500 m2. Sulfur is loaded using throw-off carriages and unloaded using two scraper reclaimers, which move along rails along the storage facilities. The warehouse is equipped with modern industrial and environmental safety systems. Sulfur is loaded at the OTEKO bulk cargo terminal onto bulk carriers with a deadweight of 15 to 120 thousand tons (Baby Capesize class), heading to Morocco, China, Brazil and other foreign countries. The design loading speed on sea vessels is up to 2.5 thousand tons per hour. When posting this information on the website of the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association, its experts considered it necessary to remind about the special "status" of sulfur in the international system of regulation of transportation of dangerous goods. Thus, in accordance with the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods and the industry rules developed on their basis, contained in the IMDG Code, ADR, ADN, RID Regulation, Annex 2 to SMGS, sulfur is defined as a dangerous goods, division 4.1 (flammable solids, self-reactive substances, solid desensitized explosives and polymerizing substances), UN number 1350. However, the Model Regulations in Chapter 3.3 "Special provisions applicable to certain articles or substances" contain special provision 242, which states the following: "Sulfur is not subject to these regulations if it has been brought to a certain form (for example, in the form of lumps, granules, tablets, plates or flakes)." Similar provisions are contained in the industry rules for the transport of dangerous goods and in the International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargoes Code (IMSBC Code). Therefore, since the application of the transport regulations for sulfur and some other bulk cargoes is not fully regulated at the international level, the relevant decisions are taken by the competent authorities. In particular, this concerns the licensing procedures for the transport of dangerous goods and the handling activities applicable to them. The rules for the transport of dangerous goods by various modes of transport are studied in detail at the training courses for Dangerous Goods Safety Advisors, held at the International Staff Training Center. The next courses will be held from 18 to 22 November 2024. | |
Maritime Security: Key to Sustainable Global Economic Development | 15.10.2024 |
     The 2024 Maritime Security Conference: Innovation and Partnership for the Future was held in Praia, the capital of the African state of Cabo Verde, from 8 to 9 October. The conference brought together global experts and leaders in the maritime industry. The participants emphasized that maritime security plays a critical role in supporting economic growth and international trade. The conference sessions addressed current and emerging threats such as drug trafficking, armed robbery at sea, transnational organized crime and terrorism. As these challenges continue to disrupt global trade routes, securing the links between ships, ports and people is more important than ever. One of the key topics of the conference was the relevance of international cooperation and innovative solutions to improve maritime security. Experts shared best practices and emphasized the value of advanced technologies such as satellite monitoring and artificial intelligence-based surveillance systems to improve coastal zone management and effectively counter threats. The main focus was on compliance with international standards. The participants emphasized the exceptional importance of compliance with the provisions of the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS 74) and the International Ship and Port Facility Security Code (ISPS Code) arising from it. The framework of these documents is important for solving the complex problems that countries face in addressing maritime security issues. It should be noted that experts from the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (IDGCA) and the International Staff Training Center (ISTC) developed and approved at the Ministry of Transport of Russia the first training programs in the country for training specialists of various levels in accordance with the requirements of this document even before the ISPS Code came into force in 2004. These programs trained specialists in the field of ship and port facility security for shipping companies in Russia and neighboring countries. Currently, the ISTC continues to train company and port facility officials responsible for security, as well as officers responsible for ship security (specialized courses). In addition, topics related to the study of the ISPS requirements are included in the following training programs:
The next training courses of IMDG Code experts will be held at the ISTC from 21 to 25 October. | |
XVIII International Conference "Multimodal Transport of Dangerous Goods - Fuel of the Future - the Path to Sustainable Development - 2024" | 11.10.2024 |

On October 8, 2024, the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association held the XVIII International Conference "Multimodal Transport of Dangerous Goods - Fuel of the Future - the Path to Sustainable Development - 2024". The head of the municipal formation of the city of Peterhof, A.V. Shifman, addressed the participants and guests of the conference with a welcoming speech, noting the high importance of this event for the country's economy, and wished the delegates successful work. The opening speech and a detailed report were made by the president of the IDGCA NP, Moshkov G.Yu. In his report, he clearly outlined the challenges facing industry and transportation in the light of the sustainable development goals and the resulting challenges in the development of advanced energy-related technologies and equipment. The conference was chaired by General Director M.I. Ognev. In his opening remarks he also noted that 2024 is a significant year for the IDGCA NP, since exactly twenty years ago the international association was awarded consultative status in the UN subcommittee of experts. This largely determined the topic of the conference and its focus, since it is the United Nations that draws special attention of all countries to the desire for sustainable development and green technologies. Executive Secretary of the Technical Committee for Standardization "Oxygen and Cryogenic Equipment" (TC 114) of Rosstandart E.A. Demidova made an interesting report on the development of standardization in the field of production of process equipment and equipment for storage and transportation of promising fuel grades. The topic of the speech of the Deputy Head of the Department of Permitting and Licensing Activities of the Interregional Territorial Administration of the Federal Service for Supervision of Transport in the North-West Federal District M.N. Grachenkov concerned the legal regulation and state supervision of the construction and operation of marine terminals for transshipment of LNG and other liquefied gases. The representative of another supervisory body, Rostransnadzor, Deputy Head of the Department for Supervision of Petrochemical and Metallurgical Facilities of the North-West Department of the Federal Service for Ecological, Technological and Nuclear Supervision, D.N. Egorova, highlighted issues related to industrial safety regulations applicable to LNG terminals. The report by D.A. Gornov, Head of the Hydrocarbon Products Sales Department of Gazprom LNG Portovaya LTD, concerning the practice of handling gas carriers at LNG marine terminals, ship-shore interactions and the duties of a cargo master, attracted great attention. Expert M.V. Shcherbatov shared his experience of working at similar terminals abroad. An interesting report on the development of a new subsection 6.9.4 "Requirements for the design, manufacture and testing of portable tanks with a vessel made of polymer composite materials intended for the transportation of non-refrigerated liquefied gases" of the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods was made by I.V. Sergeichev, Director of the Materials Technology Center of the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology. The transportation of various goods, including energy resources, along the Northern Sea Route is becoming increasingly important, so the participants and guests of the conference listened with interest to the report on this topic by the head of the Department of Transport Logistics of the Admiral S.O. Makarov State University of Maritime and Inland Shipping, Professor E.A. Koroleva. Many problems have accumulated in the field of ensuring the safety of transportation of such an aggressive substance as hydrogen peroxide, as expert A.V. Kazimirov spoke about. The conference participants and guests listened with great attention to the report of the expert I.B. Pugaev, concerning the bunkering of ships with liquefied refrigerated gas in sea ports from road tanks and tank containers. Many interesting questions were raised during the round table, where the opinions of representatives of business, scientific organizations, supervisory authorities were expressed in free communication and the problems of legal regulation in the Russian Federation were raised concerning the transportation of dangerous goods, safety requirements for offshore oil and gas terminals, requirements for the interaction of sea and river vessels and terminals. One of such questions concerned the problems associated with the stacking of tank containers with liquid hydrogen in port areas, where the requirements of industrial safety, transport safety and safety in general intersect. In all likelihood, the work of the conference will continue after its completion through the exchange of opinions, questions and letters. Many interesting questions were raised during the round table, where the opinions of representatives of business, scientific organizations, supervisory authorities were expressed in free communication and the problems of legal regulation in the Russian Federation were raised concerning the transportation of dangerous goods, safety requirements for offshore oil and gas terminals, requirements for the interaction of sea and river vessels and terminals. One of such questions concerned the problems associated with the stacking of tank containers with liquid hydrogen in port areas, where the requirements of industrial safety, transport safety and safety in general intersect. In all likelihood, the work of the conference will continue after its completion through the exchange of opinions, questions and letters. | |
The XVIII International Conference "Multimodal Transport of Dangerous Goods | 04.10.2024 |
|
3 days left until the meeting of professionals whose activities are related to the production and transportation of gases and other energy resources by various modes of transport. New promising technologies, new transport equipment and new regulations - this is what awaits guests and participants of the conference Date:October 8, 2024 The conference venue can be reached from Avtovo metro station by buses 201, 210, 351A and 359. | |
XVIII INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE "MULTIMODAL TRANSPORT OF DANGEROUS GOODS" | 27.09.2024 |
|
On October 8, 2024, the XVIII International Conference "Multimodal Transport of Dangerous Goods: Fuel of the Future - the Path to Sustainable Development - 2024" will be held. The conference program covers issues related to the production of advanced fuels, including liquefied natural gas, hydrogen, ammonia and methanol, as well as their transportation and storage. The topic of bunkering ships with refrigerated liquefied gases and new requirements for fuel preparation systems on sea and river vessels will be touched on. The conference will feature relevant reports from leading scientists, heads of transport companies, representatives of offshore oil and gas terminals, and maritime administrations. The practice of loading LNG from terminals to gas tankers will be covered by representatives of Gazprom LNG Portovaya Ltd and Cryogaz-Vysotsk Ltd. A representative of Rosstandart will make a report on technical regulation, who will talk about the development of new national and international standards regarding equipment and vehicles for the transportation of refrigerated liquefied gases. Representatives of Rostransnadzor and Rostekhnadzor will review regulatory legal acts in the field of industrial safety and transport safety. Issues of oil and gas transportation along the Northern Sea Route will be discussed, taking into account the complex geopolitical situation. Conference participants will hear a report on the development of new codes of the International Maritime Organization concerning the use of new types of fuel and regulating their transportation, and many other reports. | |
Liquefied Natural Gas Incident | 18.09.2024 |

On September 16, an explosion occurred on an LNG pipeline in La Porte, Texas, USA. According to preliminary data, a car accident may have been the cause of the explosion and the subsequent major fire on the pipeline. Authorities said that residents of about 50 houses located near the epicenter of the incident had to be evacuated. Unfortunately, this is not an isolated case when, due to the notorious "human factor", incidents, accidents and disasters with liquefied natural gas occur. In technology in general, and in its areas where LNG is produced, transported or used, especially, there are no trifles. This is due to the special physical and chemical properties of this energy source. It is necessary to remember that LNG is a cryogenic liquid, which, when it comes into contact with exposed areas of the human body, causes severe frostbite. LNG vapors mixed with air form explosive mixtures. Being a low-toxic substance, natural gas at a high concentration of its vapors in the air can affect the concentration of oxygen and cause suffocation. Currently, LNG is widely used in various transport systems as a fuel for engines, and is used in everyday life. It is on a par with such promising energy sources as hydrogen and ammonia. Due to a significant expansion of the scale of its use and, accordingly, an increase in the volumes and intensity of its transportation by various modes of transport, including pipelines, new technologies and corresponding technical solutions are in demand. Currently, experts from IDGCA NP, contributing to this important process for the country's economy, have begun to develop a new national standard regarding the design, testing and use of tank containers for refrigerated liquefied gases, including LNG. The problems of production, transportation and use of promising energy sources will be discussed at the II International Conference "Fuel of the Future - The Path to Sustainable Development - 2024", which will be held on October 8, 2024 in Peterhof. | |
Conference in Peterhof, October 8 | 06.09.2024 |
 
The city of Peterhof is famous not only for its fountains, but also for its unique nature, landscape, ponds and parks. It is no coincidence that the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (IDGCA NP) chooses Peterhof as a venue for conferences. Here, surrounded by famous park ensembles, there is an opportunity to hold a meeting of scientists, business representatives, and administrations with common interests in the issues of cargo transportation safety, accident-free operation at sea terminals, and striving for sustainable development. Responding to the requests and interests of our partners, IDGCA NP and the International Staff Training Center have again chosen the topic for the upcoming conference: "Fuel of the Future - The Path to Sustainable Development". As at the previous conference, also held in Peterhof, the main issue of discussion will be the development of new energy related to the use of new types of fuel. The issues to be discussed will include the use of new types of equipment, new standards, conditions for transporting liquefied refrigerated gases by various modes of transport in today's complex geopolitical conditions, building new vessels, chartering issues, as well as issues of regulatory framework at offshore oil and gas terminals. The issue of transporting LNG and other hydrocarbons along the Northern Sea Route will also be addressed. The agenda is so extensive that it is unlikely that each of these issues will be discussed in detail and relevant recommendations will be received, but given the level of speakers invited to the conference, its organizers hope that all participants will receive exactly the information they need. The conference will be chaired by Vice-Admiral G.Yu. Moshkov, President of the IDGCA NP, and will include representatives of the administration. Conference participants will have a unique opportunity to ask questions to representatives of supervisory authorities, scientists, and representatives of large companies. The conference will be followed by a discussion and a friendly dinner. | |
Container Ship Explosion | 14.08.24 |

According to the state television channel of the People's Republic of China CCTV and several other media outlets, on August 9, 2024, in the port of Ningbo-Zhoushan, one of the largest ports in China and the world, a powerful explosion occurred in a container on board the YM Mobility container ship moored to the berth. As a result of the explosion and the resulting fire, not only the container ship itself was significantly damaged, but also the cargo on it. According to the port authorities, none of the port workers or the ship's crew was injured. An investigation has been launched to establish the causes of the incident. Among the versions are violation of the rules for the operation and transportation of explosive substances, as well as sabotage. The YM Mobility container ship, built in 2011, belongs to the Taiwanese carrier Yang Ming and carries out cargo transportation under the Liberian flag. Its capacity is 6,589 TEU. According to the Ningbo Marine Search and Rescue Center, the ship was carrying dangerous goods. However, some sources suggest that "the exploded cargo was glycerin." The explosion at the Ningbo-Zhoushan Port is a serious incident that requires careful information gathering and investigation, which will take some time. But even now, based on preliminary data, we would like to focus on some issues. If we agree with the version that the substance that led to the incident was glycerin, it should be noted that this substance is not classified as a dangerous goods, and the requirements of the International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code (IMDG Code) do not apply to its transportation. In accordance with the interstate standard GOST 12.1.007-76 "Occupational safety standards system - Harmful substances - Classification and general safety requirements," this substance is defined as low-hazard. Glycerin is not subject to classification according to the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS). However, according to some sources, such as the European Chemical Agency (ECHA), when heated intensively, glycerin forms explosive mixtures with air. In the event of a fire, acrolein (a toxic compound that strongly irritates the mucous membranes of the eyes and respiratory tract), as well as carbon monoxide and dioxide (toxic gases) can be released. Thus, even a cursory analysis of only one of the assumptions about the causes of the incident leads to the conclusion that during transportation, especially by sea, even a completely "harmless" substance can create big problems. Every participant in the sea transportation process (shipper, carrier, consignee), as well as officials of control and supervisory authorities, should know and apply this in practice. When preparing any cargo for shipment and developing transport documentation, it is necessary to carefully consider the specifics of each cargo, especially chemical products, take into account the features of the upcoming transportation, the natural and climatic conditions of the relevant regions, etc. Awareness of the importance of the above comes only to personnel who regularly undergo professional training and certification in organizations whose teaching staff is directly involved in the development and improvement of international and national rules for the transportation of both dangerous and other types of cargo that are potentially dangerous during transportation, especially by sea. The International Staff Training Center (ISTC) regularly and at a high professional level conducts training for IMDG experts, ADN experts and Dangerous Goods Safety Advisors. This significantly helps to reduce the risk of accidents with dangerous goods due to the fault of the crew and personnel of companies whose activities are related to dangerous goods. Experts of the independent survey company ZAO Russian Register are also always ready to assist shippers and carriers by providing consultations and other assistance in preparing transport documents and assessing the compliance of dangerous goods prepared for transportation with the requirements of international conventions and regulations. | |
ADN training | 15.07.2024 |

The ADN rules are a unique international instrument for regulating the transport of dangerous goods on inland waterways. The peculiarity of transporting dangerous goods along rivers is that any incident (explosion, fire, spill of dangerous goods) can cause irreparable damage to the coastal structure and residents of coastal areas. The ADN rules are consolidated rules that establish requirements for the technology of transporting dangerous goods, as well as requirements for ships that transport dangerous goods. Compared with seagoing vessels, river vessels subject to ADN have a crew of 3-4 people, which requires the ship's crew to perform many tasks, including safety operations for handling dangerous goods. The basic course includes studying the requirements for the transport of dangerous goods on dry cargo ships and tankers. The ISTC conducts training not only for representatives of Russian but also foreign shipping companies. Training is carried out at the ISTC, and certification on a voluntary basis is carried out at the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association. As opposed to the requirements of the IMDG Code, the SOLAS Code and other conventions, the ADN rules spell out requirements for classification societies. The next basic training courses will be held at the ISTC from July 22 to July 26, 2024. | |
Self-regulation in sea and river transport | 28.06.2024 |
 
Officials of the Ministry of Transport of Russia supervising sea and river transport have made repeated attempts to introduce mandatory self-regulation in sea and river transport. But this idea was not supported by both government authorities and business. In world practice, such concepts as "mandatory self-regulation" and "self-regulatory organizations" do not exist. Of course, all over the world there are non-profit organizations, in particular, associations that unite business structures and protect their interests, including from excessive government regulation, which can lead to significant costs for businesses. The Russian Marine and River Bunker Operators Association has repeatedly attempted to introduce mandatory self-regulation of bunkering activities in sea and river transport. Back in 2013, its leadership addressed a letter on this issue to the Chairman of the Government of the Russian Federation D.A. Medvedev, but did not receive a positive response. Before the release of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation ? 2111 dated November 30, 2021, which approved the Regulations on licensing handling activities in relation to dangerous goods in inland water transport, in seaports, which abolished the licensing of bunkering activities, this activity was regulated precisely by licensing, which is sufficient degree ensured the safety of bunkering operations and did not create large expenses for bunkering companies. This activity was related to handling activities in relation to dangerous goods. With the release of this Decree, bunkering activities were separated from handling activities and, as it became clear from the draft Federal Law "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation", presented by the Ministry of Transport of Russia, bunkering activities should be transferred to the sphere of mandatory self-regulation. According to the managers and specialists of bunkering companies, notable for their discipline and high quality of work performed, mandatory membership in a self-regulatory organization (SRO) will entail significant financial expenses for companies associated with the payment of a compensation fee (presumably 500 thousand rubles), monthly payment of membership fees and compulsory insurance. At the same time, as the practice of self-regulation in other areas, in particular in construction, has shown, compensation contributions, as a rule, are not used for their intended purpose (to compensate for the costs associated with the provision of poor-quality services, especially to compensate for damage to any party), on the other hand, the business is constantly subject to all kinds of inspections by the SRO and is faced with the obligation to fulfill all sorts of additional conditions, which is unlikely to have a positive effect on the quality of services provided by SRO members. In the draft Federal Law, the interests of the parties and who the beneficiaries are, are quite clear and clearly visible: first of all, these are certain administrative structures, banks and insurance companies, as well as the rather monopolized Russian Association of Sea and River Bunker Operators, which is an ardent supporter of self-regulation in the field bunker business. If the Federal Law is adopted, unreasonable expenses will be incurred not only by business, but also by state supervisory authorities, for example Rostransnadzor, which, obviously, will be the body supervising the activities of SRO, which will require additional staff. Self-regulation does not in any way cancel state regulation, including on the part of Port Administrations, as well as their responsibility for the quality and safety of bunkering operations. It is completely unclear for what purposes the funds from the compensation contribution will be used. At least, few people can say which damage from which accident was covered from the compensation contribution and when. According to experts from the IDGCA NP and representatives of bunkering companies who have familiarized themselves with the draft Federal Law, it can be seen as a violation of the legislation on the protection of competition and a corruption component. Generally speaking, in accordance with Russian legislation in the field of self-regulation, membership in an SRO is voluntary, and the main task of such an organization is to support, and not suppress business and create financial and regulatory problems for it. The "cock wheel" between government regulation and the activities of bunkering companies will not bring any benefits to business and, according to experts, will not contribute to improving safety. To ensure safe and high-quality work of bunkering companies, a license for bunkering activities with appropriate mandatory training of personnel in this area is sufficient. World practice shows that companies invest their money in professional training and certification of personnel, and this practice is effectively supported by states. In this context, it seems quite strange that the Regulations on licensing handling activities in relation to dangerous goods in inland water transport and seaports, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation ? 2111 dated November 30, 2021, does not contain any requirements for the training of personnel involved in loading and unloading operations in relation to dangerous goods. The authors of the idea of self-regulation in the bunkering business instead propose that companies pay a compensation contribution in the amount of 500 thousand rubles. For this money, you can train many qualified employees, thereby improving both the quality of services and work safety. The authors of the idea of self-regulation also touch on the issue of uniform standards for bunkering activities, and this, of course, should be viewed positively, but let us recall that standards, unlike technical regulations, must be applied voluntarily, as is customary in international practice. | |
LNG: fuel energy development strategy | 18.06.2024 |

For Russia, as for other countries, LNG production is a priority task for economic development. The production of LNG requires a developed infrastructure to ensure the extraction, transportation, production and storage of this energy carrier. For Russia, as for other countries, LNG production is a priority task for economic development. The production of LNG requires a developed infrastructure to ensure the extraction, transportation, production and storage of this energy carrier. However, for the dynamic development of the LNG industry, the old infrastructure cannot be used; it is necessary to create a new one based on modern standards. Only highly qualified personnel, whose professional training programs should include an in-depth study of international norms and standards, will be able to operate such infrastructure. The industry must master the production of new equipment designed to operate at temperatures of - 163´┐ŻC and below. It is also urgently necessary to develop and adopt regulations, rules and requirements regulating the production, transportation, storage, transshipment and regasification of LNG. Understanding the relevance of the tasks in the execution of national projects for the production and supply of LNG, the International Staff Training Center has developed and mastered new training programs for specialists working at LNG facilities;
Issues related to the prospects for the development of the LNG industry will be discussed at the XVIII International Conference "Multimodal Transport of Dangerous Goods" under the motto "Fuel of The Future - The Way to Sustainable Development - Logistics, Safety, and Ecology", which will take place on October 8, 2024 in Peterhof. The conference will also discuss other important issues of energy development, including alternative, and inextricably linked problems of environmental safety. | |
64th session of the UN ECOSOC Subcommittee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods | 07.06.2024 |
|
From June 24 to July 3, 2024, the 64th session of the UN ECOSOC Subcommittee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods is being held at the Palais des Nations (Geneva, Switzerland). The event program is very rich. In the part relating to substances and products of hazard class 1 (explosives), issues related to certain provisions of the UN Manual of Tests and Criteria, standard detonators, revision of requirements for packaging and transportation of ammonium nitrate emulsions will be considered. Of particular interest is the planned discussion of the impact of electrical energy sources and alternative fuels used in vehicles on the safety of transporting explosives. Issues related to the list of dangerous goods, their classification and packaging will be considered. Much attention will be paid to electrical energy sources (lithium battery testing, hazard classification of lithium batteries, transportation requirements, handling of damaged or faulty lithium batteries, sodium-ion batteries). A discussion is planned on issues related to the global recognition of UN pressure vessels and pressure vessels of structures that are not members of the UN. When considering amendments to the UN Model Regulations for the Transport of Dangerous Goods, issues of marking and danger signs, requirements for containers, including those made from recycled plastic materials, and the use of portable tanks will be discussed. It is undoubtedly important to discuss ensuring global harmonization of requirements for the transport of dangerous goods on the basis of the UN Model Regulations for the Transport of Dangerous Goods, issues of cooperation with the IAEA, the guidelines of the UN Model Regulations for the Transport of Dangerous Goods, their unified interpretation and implementation. Issues related to the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (testing of oxidizing substances, comprehensive classification of physical hazards and possible combinations of hazards of chemical products) are brought up for discussion among experts. Considerable attention will be paid to issues related to personnel training on the safety of handling dangerous goods. The UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development will also be discussed. In addition, other important issues will be considered. The session will be attended by General Director of IDGCA, M.I. Ognev. | |
Plenary session of the Technical Committee of the International Organization for Standardization ISO/TC 220 - Cryogenic vessels | 06.06.2024 |
 
On June 12, a plenary session of the Technical Committee of the International Organization for Standardization ISO/TC 220 - Cryogenic vessels will be held in Berlin. Many issues are on the agenda, including approval of the report of the previous session, review of the ISO Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct, report of the ISO/TC 220 technical committee secretariat, review of the status of the committee's work program and strategic business plan, follow-up to the last committee meeting, review of new ISO/IEC directives. Reports from the following working groups will also be presented:
Standardization, together with Technical Committee ISO/TC 268 "Sustainable cities and communities", will present a report on the adoption of ISO standards at European level. The meeting will consider issues of interaction with other ISO technical committees (ISO/TC 67/SC 9 "LNG plants and equipment", ISO/TC 197 "Hydrogen technologies"). As part of the consideration of the interaction of the technical committee with external organizations, reports from the European Industrial Gas Association (EIGA) and the Middle East Gas Association (MEGA) will be heard. In addition, other issues will be considered and the date and location of the next meeting will be determined. The plenary session will be attended by experts from the IDGCA NP, who, since 2004, represent GOST R in the Technical Committee ISO/TC 220. Since the beginning of 2024, experts from the Association have taken part in the development and adjustment of 8 international standards for cryogenic vessels. ISO international standards for cryogenic technology are essential for the development of modern production of liquefied natural gas and other cryogenic liquids. The study of these standards is included in many personnel training programs according to which students of the International Staff Training Center are trained. | |
What is high consequence dangerous goods? | 24.05.2024 |
 
Due to the aggravation of the geopolitical situation in the world, high consequence dangerous goods are of particular importance for all business entities and regulatory authorities, since they must be distinguished from "ordinary" dangerous goods, the provisions of which are set out in the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods and the industry regulations based on them. The International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (IDGCA NP), together with the International Staff Training Center, has prepared a special training program for working with high consequence dangerous goods. The concept of "high consequence dangerous goods" is included in almost all international and national rules for the transportation of dangerous goods, and the essence of this concept is that these goods can be used for terrorist purposes. The volume of the specialized training program is 24 academic hours, however, persons who have completed training as a Dangerous Goods Safety Advisor can obtain certificates of competence in the field of handling high consequence dangerous goods after training in an 8-hour program. IDGCA NP constantly advises business representatives and supervisory authorities regarding the application of certain international and national norms and regulations. Such consultations are always carried out on the basis of in-depth analysis and knowledge, and for this purpose both theoretical knowledge and practical experience of working with dangerous goods of the Association's experts with over 20 years of experience are used. Association's experts with over 20 years of experience are used. It is no coincidence that the International Staff Training Center trains not only representatives of business entities, but also representatives of government supervisory and control bodies. | |
NOVATEK strives for import substitution | 16.05.2024 |

The consequences of the sanctions against Russian enterprises are forcing them to look for new ways to solve problems. It recently became known that the Chinese turbine manufacturer Harbin Guanghan Gaz Turbine will not be able to fulfill an order from NOVATEK PAO to supply equipment for the second stage of the natural gas liquefaction plant of the Arctic LNG-2 project. Initially, the turbines were supposed to be supplied by the American manufacturer Baker Huges, but due to certain circumstances, only four LM-9000 turbines were delivered, after which deliveries stopped. After this, NOVATEK PAO turned to the Harbin Guanghan Gaz Turbine company, but this company could not provide guarantees on the delivery time of the equipment. In 2022, NOVATEK PAO began negotiations with Siloviye Mashiny (Power Machines) enterprise, which initially assumed that, since all turbines had already been contracted, this equipment could be delivered for the Arctic LNG-2 project no earlier than 2025. However, the plans were adjusted, and information appeared that the first turbine would be shipped this year. Another serious problem for NOVATEK PAO is the lack of an LNG tanker fleet, which is holding back LNG production from existing projects, and global LNG producers have taken advantage of this by dramatically increasing their production capacity. It is worth noting that thousands of Russian and foreign companies participated in the design and construction of the production complex for the Arctic LNG-2 project, and billions of dollars were invested in the development of the project. National Bureau of Expertise Ltd. (NBE Ltd.), a member of the IDGCA NP, has also participated in the construction of technological modules for LNG production for more than 10 years, both for the Yamal LNG project and for the Arctic LNG project. 2. All technological modules were manufactured at various enterprises in China. An important and responsible operation was the execution of installation supervision work on installation and debugging of fire-fighting equipment and electrical equipment on technological modules. To perform these works, a license from the Ministry of Emergency Situations and membership in a self-regulatory organization is required. NBE Ltd. fully fulfilled its tasks, even during the coronavirus pandemic. All technological modules were received in China and delivered to the installation site. The experience gained by employees of NBE Ltd. while working on the Arctic LNG-2 project was used in the development of joint training programs for specialists to work at LNG terminals. On a regular basis, the International Staff Training Center conducts training for managers and engineers planning to work and working at LNG production and shipping enterprises. The training programs also involve the study of updated international standards, the development of which is carried out quite intensively on the basis of the International Organization for Standardization. | |
New edition of the international standard | 14.05.2024 |

As part of their work in the Technical Committee of the International Organization for Standardization ISO/TC 220 "Cryogenic vessels", experts from IDGCA NP analyzed the draft amendments to the international standard ISO/DIS 21013-2 "Cryogenic vessels - Pressure-relief accessories for cryogenic service - Part 2 : Non-reclosable pressure-relief devices". The changes concern issues related to ensuring the compatibility of structural materials of pressure relief devices with the working fluids contained in cryogenic vessels, which is of particular importance in cryogenic technology, especially for substances such as oxygen and hydrogen. The experts approved the project and sent a positive decision to vote for it. Since the beginning of 2024, this is already the seventh draft of international standards relating to cryogenic vessels and their equipment, which has been reviewed by the IDGCA NP.Work at ISO significantly helps to improve the training programs of ISTC for specialists in a number of specialties, in particular, loading masters and loading operators of LNG marine terminals. At the request of Rosstandart, experts from the IDGCA NP translated 23 ISO standards for cryogenic vessels into Russian, which will significantly contribute to the development of domestic cryogenic technology. | |
The inspection staff of Rostransnadzor improves their professional skills in the field of transportation of dangerous goods by sea and inland waterway transport | 13.05.2024 |

No democracy can imagine its existence without specially trained government officials performing the functions of government supervision and control. In international and national regulations that define the requirements for the transportation of goods, and, first of all, dangerous goods, such bodies are defined as the competent authorities or administrations of states that are entrusted with supervision and control at all stages of the transportation of goods and passengers, as well as the production of vehicles and transport equipment. Almost all international conventions and agreements require mandatory specialized training for supervisory authorities in the area under their control. And this is regardless of whether these authorities delegate certain powers to private inspection bodies or not. Supervisory authorities must be higher in their competence than the organizations they supervise. Understanding the above, IDGCA NP and ISTC with great responsibility approach to the formation of training programs for officials of supervisory authorities depending on their areas of competence. At ISTC, training of employees of control and supervisory bodies is carried out on an ongoing basis. In addition to Rostransnadzor employees, officials from customs authorities, seaport administrations, as well as designated persons carrying out control and supervisory functions at enterprises undergo such training. The next advanced training courses for officials of the Federal Service for Supervision in the Sphere of Transport (Rostransnadzor) are held at the ISTC from May 13 to May 17. During the course, Rostransnadzor inspectors will study international and national documents regulating the transportation and handling of dangerous goods in maritime and inland waterway transport, in their latest editions, and will also gain practical skills in working with these documents. Officials of interregional territorial directorates of Rostransnadzor in all Federal Districts of the Russian Federation were sent to the courses. | |
Bunkering of ships is a dangerous type of activity | 27.04.2024 |
 
Paragraph 3 of the regulation on licensing handling of dangerous goods in inland water transport and seaports, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 30, 2021 № 2111 excluded bunkering operations from the list of works on handling of dangerous goods, which subject to licensing. Since the entry into force of this Regulation, organizations that carry out bunkering operations in sea and river ports got caught up in a situation of uncertainty: handling of petroleum products and LNG is subject to licensing, but bunkering of ships with the same dangerous products with the same risks of emergency situations, water pollution, etc. is not licensed. In addition, this type of activity does not fall under the requirements of the Federal Law ´┐ŻOn Industrial Safety of Hazardous Industrial Facilities´┐Ż dated July 21, 1997 №116-FZ (as amended on November 14, 2023). As statistics of major incidents related to bunkering have shown, sea pollution, accidents and fires most often occur due to the lack of sufficient training of employees and managers of companies involved in bunkering. The only way to increase the safety and awareness of personnel at such facilities is through staff training. In this regard, experts from the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association,together with the International Staff Training Center, have developed a training program for advanced training ´┐ŻBunkering operations in sea and river ports´┐Ż of 40 academic hours. The program is intended for management and engineering staff of enterprises involved in bunkering sea and river vessels with both petroleum products and LNG. This program is basic and can be adapted to the needs of specific ports and terminals. The program covers many current issues (topics), including: various bunkering schemes, basic properties of marine fuels (including LNG), technological equipment used during bunkering operations, interaction between tanker and terminal, technology for bunkering with petroleum products and LNG, oil and petroleum products spill prevention and response, risk management during bunkering operations, etc. Training and the final exam are conducted in a combined format: both in the classroom and remotely, in real time, using telecommunications technologies. Graduates who successfully pass the exam and receive certificates of advanced training are certified by the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association and are awarded international certificates. Experts from the independent survey company Russian Register Ltd. (ZAO Russkiy Register), whose specialists have been carrying out bunker surveys on Russian and foreign vessels for more than 20 years are invited to conduct practical training in the courses. | |
When hazardous waste can become dangerous goods | 22.04.2024 |
 
In accordance with the Federal Law of June 24, 1998 ´┐Ż 89-FZ ´┐ŻOn Production and Consumption Waste´┐Ż (as amended as of August 4, 2023), activities for the collection, transportation, processing, recycling, neutralization, and disposal of waste of I-IV hazard classes are subject to licensing in accordance with Federal Law of May 4, 2011 ´┐Ż 99-FZ ´┐ŻOn licensing of certain types of activities.´┐Ż It is worth paying attention to the fact that in accordance with the rules to the European Agreement Concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) (document ECE/TRANS/326), UN, New York and Geneva, 2023 that apply on the territory of the Russian Federation as national rules, dangerous goods are divided into 13 hazard classes. As a result, there is confusion between the categories of ´┐Żhazardous waste´┐Ż and ´┐Żdangerous goods.´┐Ż Persons who are approved for all types of work with waste of I-IV hazard classes and its transportation must have qualifications certificates issued based on the results of professional training. Training is conducted according to training programs based on the standard additional professional program approved by Order ´┐Ż 755 of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Ecology of the Russian Federation dated October 15, 2021, with a volume of 38 academic hours. Both the standard program and the programs developed on its basis and implemented in various institutions of additional professional education do not include issues related to the classification and features of handling dangerous goods. Therefore, the personnel involved in the collection, processing and transportation of hazardous waste, having only general training in waste management, are not knowledgeable about issues related to the handling of dangerous goods, which causes substitution of concepts, misunderstandings and creates the preconditions for bringing operators to administrative responsibility for violating the rules on transportation of dangerous goods, which are not the same as hazardous waste, as it defined in Federal Law ´┐Ż 89-FZ. At the same time, control and supervisory authorities have certain grounds for such actions due to the fact that the operator does not always see the difference between dangerous goods and hazardous waste. Taking into account the above, experts from the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (IDGCA NP), together with teachers from the International Staff Training Center (ISTC), have developed a training program for advanced training of specialists involved in the handling of hazardous waste. The program takes into account the peculiarities of handling both hazardous waste and dangerous goods, at all stages of their life cycle. The volume of the training program is 40 academic hours. Mastering this expanded training program will allow both managers and operators involved in the collection, processing and transportation of hazardous waste to gain new competencies, as a result of which operators will perform their work more reasonably, and cases of groundless claims against them from control and supervisory authorities will be excluded. | |
Russia is the first country in the world to send a man into space | 11.04.2024 |
 
On April 12 we celebrate Cosmonautics Day. The history of domestic and world cosmonautics goes back decades. This story includes both victories and tragic events, but one thing is certain ´┐Ż cosmonautics is developing, and more and more countries are becoming space-faring nations. No matter how the history of cosmonautics develops, the flight of Yuri Alekseevich Gagarin will forever remain an incomparable event. It was our country that took a step into the unknown. Rocket and space technology is constantly devolving. Now on the agenda is the issue of using advanced fuels for space rockets, for example, both research and development work on rocket engines using liquid methane as fuel is being carried out, and practical results have been obtained. On the eve of Cosmonautics Day, the Angara-A5 heavy-class rocket successfully launched from the Vostochny Cosmodrome. This event opens up broad prospects for domestic cosmonautics. In particular, the modernized Angara-A5M will be able to launch modules of the new Russian orbital station into orbit. At the same time, in the near future, an upper stage with oxygen-hydrogen engines will be developed for the Angara family. Issues related to advanced rocket fuels for peaceful space will be discussed, along with other issues, at the II International Conference ´┐ŻFuel of the Future ´┐Ż The Way to Sustainable Development, 2024 ´┐Ż Logistics, Safety, and Ecology´┐Ż, which will be held on June 4, 2024 in Peterhof. | |
Operator of small-scale LNG production facilities | 05.04.2024 |

The International Staff Training Center (ISTC) has accumulated significant experience in training loading masters of LNG marine terminals. A logical continuation of this work was was the development of a new training program designed to train operators of small-scale LNG production and regasification facilities. The relevance of the program is caused, first of all, by the fact that small-scale LNG production has received significant development in recent years in accordance with the "Action Plan for the development of the market for small-scale liquefied natural gas and natural gas motor fuel in the Russian Federation until 2025", approved by the Order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 13 February 2021 ? 350-p. Small-scale LNG production enterprises built to date use various facilities that implement throttle, expander, combined cycles, as well as nitrogen cooling technologies. Consumers of small-scale LNG production products are various enterprises and industries, including autonomous power generation facilities, gasification enterprises for populated areas, transport (use as gas motor fuel), etc. Some of the products are intended for export supplies. A distinctive feature of the ISTC training program is that it is extremely specific, selecting exactly the training material that operators of small-scale LNG production and its regasification facilities will need in their practical activities. This training material is based on the provisions of international requirements and standards in the field of cryogenic technology and the requirements of the national regulatory framework. Training classes are conducted by experienced teachers, including doctors and candidates of technical sciences, academicians of the International Academy of Refrigeration, practitioners with extensive experience in the field of cryogenic equipment and cryogenic technologies. Course graduates will receive new competencies necessary to ensure trouble-free operation of production facilities. | |
Marine LNG Terminal Loading Master | 29.03.2024 |

The International Staff Training Center (ISTC) has completed training for the next group of students under the "Marine LNG Terminal Loading Master" program. Marine LNG terminals are facilities that include complex process equipment, the safe operation of which is ensured only with a high level of professionalism of the personnel, among which loading masters occupy a central place. The training program covers a wide range of issues, including the study of international conventions, codes, rules, national regulatory frameworks, study of the properties of LNG, detailed consideration of practical issues related to the interaction of a gas tanker and a terminal, preparation of process equipment for operation (taking into account the fact that LNG is a cryogenic liquid), ensuring safety during all types of work at the terminal, instilling practical work skills, including with operational documentation, etc. The training program uses materials from the ISO standards, in the development of which experts from the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (IDGCA) take part, working in the Technical Committee ISO/TC 220 - Cryogenic vessels. Despite the high intensity of the program, the exceptional professionalism of the ISTC teachers, among whom there are sea captains, employees of the Ministry of Emergency Situations, specialists with experience in working at terminals, including offshore ones, and representatives of the teaching staff of universities, ensures that students learn the educational material in the shortest possible time. Each marine LNG terminal has its own characteristics, which add specificity to the functional responsibilities of the personnel and, above all, loading masters. The issues and content of educational topics of the program are adjusted accordingly. Based on the results of training at the ISTC, students successfully passed the final exam and received certificates of advanced training, as well as Marine LNG Terminal Loading Master certificates. | |
The new edition of the UN Model Regulations for the Transport of Dangerous Goods in Russian has arrived in the library of "IDGCA" NP | 26.03.2024 |

The Secretariat of the UN ECOSOC Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods and the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (hereinafter referred to as the Committee) sent to the International Dangerous Goods and Container Association ("IDGCA" NP) the Russian version of the 23rd revised edition of the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods (document ST/SG/AC.10/1/Rev.23). As is known, the Model Regulations are revised once every 2 years. First of all, this is due to the fact that new goods appear that are not covered by the lists of dangerous goods of previous editions of the regulations, new technologies for the transportation and handling of dangerous goods are being developed and implemented, and new problems of ensuring safety during the transportation and handling of dangerous goods are being revealed. The amendments to the Model Regulations included in their 23rd revised edition, approved by the Committee at the 11th session on 9 December 2022, relate to the following: a) New UN numbers and provisions governing the transport of sodium ion batteries, extinguishing agent dispersal devices, disilane, gallium contained in the articles and trifluoromethyltetrazole sodium salt in acetone; b) Tightening the conditions for the transport of tetramethylammonium hydroxide, including the creation of a new UN number for concentrations of at least 25%; c) Changes to the provisions governing the transport of battery-powered vehicles, including the creation of three new UN numbers; d) Exemption for the carriage of prototypes and a limited number of industrial prototypes of cells or batteries; e) A new special provision regulating the increase in the permitted volume of carriage in limited quantities of certain compressed gases of Class 2.2 without additional hazard; f) More specific limit values for hot concentrated solutions of ammonium nitrate; g) Exemptions for nitrocellulose membrane filters used in rapid testing devices, for example, for pregnancy, COVID-19 infection or other infectious diseases; h) Clarification of pharmaceutical products (such as vaccines) in ready-to-use form; and i) A reasonable version of the requirements in the case of the use of recycled plastics in containers. The Dangerous Goods Safety Advisers training course, which will be held from 8 to 12 April 2024, will feature a presentation of the new amendments included in the 23rd revised edition of the UN Model Regulations for the Transport of Dangerous Goods. | |
Dangerous Goods Safety Advisers are required by all companies involved in the transport and handling of dangerous goods | 26.03.2024 |

During the period from March 18 to March 22, 2024, courses for training Dangerous Goods Safety Advisers were held at the International Staff Training Center (ISTC). The classes were conducted in a combined format (classroom classes combined with classes using a telecommunications platform). Final exams were held in the same format. Based on their personal applications graduates are presented for certification as advisers in the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (IDGCA). In the near future, they will be sent a new type of Dangerous Goods Safety Advisers certificates protected by a patent, and information about the advisers will be posted on the official website of the IDGCA. Employees of the following companies completed the courses: Ust-Luga Container Terminal AO, Balteko Ltd., and Caspian Shipping Lines Ltd. The next Dangerous Goods Safety Advisers training course will be held from 8 to 12 April and will specifically address the latest changes to the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. | |
The Safety Advisor on the Transport of Dangerous Goods training program is continually being improved | 29.02.2024 |

Experts from the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association conducted an in-depth analysis of the current international regulations relating to the transport of dangerous goods by road, inland waterway, rail and sea transport, as well as relevant national legislation and standards, and came to the conclusion that there are discrepancies and contradictions that may affect the quality of multimodal transport. This concerns, for example, the concepts of "classification code" and "classification number", marking in the form of orange plates and certain differences in the interpretation of a number of provisions in international and national rules. Taking these circumstances into account, a specialized training program has been prepared for specialists who organize the transportation of dangerous goods by multimodal transport. This program is an addition to the existing Dangerous Goods Advisor training program and participants will be able to navigate the application of national and international regulations by completing the updated course. Updated advisor training courses will be held in ISTC from 18 to 22 March. | |
Translation of international standards | 19.02.2024 |
 
On behalf of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology (Rosstandart), experts from the IDGCA NP are completing the translation into Russian of more than 23 international standards developed and adopted within the framework of the activities of the technical committee of the International Organization for Standardization ISO/TC 220 "Cryogenic vessels", in the work of which the Association is directly involved. To carry out translation and editing of Russian-language texts of standards, IDGCA NP created a working group, which included experts specializing in the field of cryogenic technology, industrial safety, materials science and applied fields. The activities of the working group do not replace the activities of the national technical committee for standardization "Oxygen and cryogenic equipment" (TC 114) and the activities of the working groups that are part of the technical committee ISO/TC 220, but allow the development of opinions on a particular standard and harmonization of national requirements with international ones. Taking these circumstances into account, a specialized training program has been prepared for specialists who organize the transportation of dangerous goods by multimodal transport. This program is an addition to the existing Dangerous Goods Advisor training program and participants will be able to navigate the application of national and international regulations by completing the updated course. Updated advisor training courses will be held in ISTC from 18 to 22 March. | |
REQUIREMENTS DEVELOPED BY THE INTERNATIONAL MARITIME ORGANIZATION TO ENSURE THE SAFE TRANSPORTATION OF CONTAINERS | 12.02.2024 |

The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has long worked to ensure the safe transport of containers, including developing container stowage guidelines, mandatory SOLAS requirements to provide verified gross mass of a container before it is loaded onto a ship, mandatory reporting of container loss (amendments to the SOLAS and MARPOL conventions will be adopted in 2024). According to IMO information, the International Maritime Organization has developed and adopted a number of requirements to ensure the safe transportation of containers, and also developed special guidelines for packaging and securing cargo in containers. The IMO International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), in Chapter VI on the carriage of goods, includes requirements for the stowage and securing of cargo or cargo units (for example, containers). The International Convention for Safe Containers (CSC) establishes test procedures and relevant strength requirements for containers. The International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code is a mandatory international code for carriage of packed dangerous goods by sea enhancing and harmonizing the safe transport of dangerous goods and preventing environmental pollution. The Code sets out in detail the requirements applicable to each individual substance, material or article, and covering packaging, containerization and stowage, with particular emphasis on the separation of incompatible substances. IMO, together with the International Labor Organization (ILO) and the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), have developed a non-binding global code of practice for the handling and packaging of cargo transport units, which can be applied equally to both maritime and land transport. The CTU Code is currently being revised by the three above-mentioned bodies in cooperation with the industry. In addition, IMO has also adopted the Code of Safe Stowage and Securing Practice (CSS Code). In connection with the transport of CTUs, at the request of IMO, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has revised the relevant ISO standards (ISO 1161: Series 1 freight containers - Corner fittings - Specifications; and ISO 3874:2017: Series 1 freight containers - Handling and securing) to introduce the latest advances in container handling and securing equipment, taking into account the latest generation of container carriers with a design capacity of more than 18,000 TEU, as well as the design and strength characteristics of automatic twistlocks. On July 1, 2016, requirements for verification the gross mass of a loaded container in accordance with the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) came into force. Knowing the exact gross mass of a loaded container is critical to ensure proper stowage and stacking, and to prevent stacks of containers from collapsing or being lost overboard. This is an important safety measure designed to protect lives and prevent injury and destruction of property. SOLAS has always had a requirement to declare the gross mass of cargo and containers, but the so-called verified gross mass rule has added additional requirements for mass verification. This is necessary to ensure that the shipper's declared mass accurately reflects the total mass of the loaded container. The basics of the safe transportation of dangerous goods in containers, international conventions CSC-72 and CTC-72, ISO standards for containers are studied at the International Staff Training Center (ISTC) by course participants in the "Safety Advisor on the Transport of Dangerous Goods" program. The next courses under the program "Safety Advisor on the Transport of Dangerous Goods" are planned from March 18 to March 22, 2024. The III Congress of Safety Advisors on the Transport of Dangerous Goods will take place on September 26, 2024. | |
New 10th revised Edition of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) | 01.02.2024 |

The International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association received the 10threvised edition of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), sent by the UN Secretariat to IDGCA in Russian, for the library. While the GHS is primarily intended for government and regional agencies, it also provides sufficient context and includes guidelines for industry personnel who will ultimately ensure compliance. The availability of information on chemical products, their associated hazards and how to protect people will provide the basis for the development of national programs for the safe handling of chemical products. The widespread implementation of good chemical management worldwide will better protect the world's people and the environment without limiting the benefits of chemical products. Harmonization in this area will also have a positive impact on the facilitation of international trade by providing greater consistency in the national requirements for chemical hazard classification and information that must be met by enterprises involved in international trade. The GHS is one of the most important documents that trainees study in the course of the International Training Centre's Dangerous Goods Safety Adviser program.The next Congress of Dangerous Goods Safety Advisers will be held on April 2, 2024. | |
On the location of storage facilities for certain dangerous goods in port areas | 11.01.2024 |

In accordance with Federal Law No. 613-FZ dated 19.12.2023 "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation", subparagraph 2) of paragraph 15 of Article 65 of Federal Law No. 74-FZ dated 03.06.2006 "Water Code of the Russian Federation", which defines prohibitions on certain types of activities within the boundaries of water protection zones, is formulated as follows (change in italics): 2) placement of cemeteries, cattle burial grounds, disposal facilities for production and consumption waste, chemical, explosive, toxic, poisonous and toxic substances (except for specialized storage facilities for ammonia, methanol, ammonium nitrate and potassium nitrate on the territories of seaports, the list of which is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation, outside the boundaries of coastal protective areas), radioactive waste disposal sites, as well as contamination of the territory with pollutants whose maximum permissible concentrations of which in waters of water bodies of fishery significance have not been established. In accordance with the definition of paragraph 11 of Article 65 of the Water Code of the Russian Federation, the width of the coastal protective area is established depending on the slope of the water body's shore and is thirty metres for a reverse or zero slope, forty metres for a slope of up to three degrees and fifty metres for a slope of three degrees or more. Thus, based on the decision of the Government of the Russian Federation, specialized storage facilities for ammonia, methanol, ammonium nitrate and potassium nitrate may be located on the territory of a seaport at a distance of 50 metres or more from the shore. In order to make an informed decision, storage projects must undergo state environmental expertise. This provision came into force on 30 December 2023. According to the IDGCA experts, the need to amend the Water Code of the Russian Federation is dictated by a significant increase in the volume of hazardous cargo transportation, including ammonium nitrate, through Russian seaports. As is known, many cargo flows have changed their directions, and many of them have left Baltic ports. At the same time, changes in the Water Code will require changes in the existing regulatory framework governing the transshipment of dangerous goods in seaports. It should be noted that many documents included in this regulatory framework are outdated and do not comply with international regulations. The International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association has repeatedly proposed a revision of the regulatory documents governing the carriage of dangerous goods by sea and river. | |
Important events in 2024 | 26.12.2023 |
|
On April 2, 2024, the III Congress of Dangerous Goods Transport Safety Advisors will be held in St. Petersburg. The most important tool for improving the safety and quality of dangerous goods transport by various modes of transport is the presence of company officials responsible for the transport of dangerous goods. As a rule, these are employees who have get special training and experience and knowledge that meet the requirements for a dangerous goods transport safety advisor. Having an advisor is necessary not only in companies that transport dangerous goods, but also in those companies that prepare the goods for transport, store and handle them. For more than 20 years, the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (IDGCA), which has the International Personnel Training Centre (ISTC), has been training and certifying such specialists with the title of advisor. The Congress program will include exchange of opinions of the participants, analysis of international regulations and issues of harmonization of national requirements with international ones, review of current problems related to the transportation of dangerous goods and changes in logistics chains, speeches of advisors from different regions of the country. Representatives of state supervisory authorities, whose activities are related to the transport and handling of dangerous goods will also be invited to the Congress, many of whom have also been trained at ISTC. We invite you to take part in the important event. On June 4, 2024, the IInd International Conference dedicated to alternative fuels will be take place as part of the annual International Conference "Multimodal Transports of Dangerous Goods" under the motto "Fuels of the Future - the Path to Sustainable Development". The first conference on this topic successfully held on May 30, 2023 in Peterhof, attracted the attention of managers of the largest Russian companies engaged in the production, transportation and shipment of such fuels as liquefied natural gas, hydrogen, ammonia, methanol and others. The industry has recently taken a step further in this area, especially in terms of developing new regulatory requirements for the design, construction of new plants and terminals, manufacturing of new types of equipment and creation of new logistics chains, taking into account today's geopolitical situation. In this regard, many of our partners supported the initiative to organize a similar conference in 2024 at the same venue in Peterhof. We hope to see you among the participants of the forthcoming conference to discuss topical issues on this subject. | |
Methane as fuel for space rockets | 13.12.2023 |
According to a number of media reports, the People's Republic of China successfully launched a Landspace rocket. The main feature of this rocket, which put into orbit three satellites, is that it uses liquid methane as rocket propellant, while the oxidizer is liquid oxygen. This is the third launch of the Zhuque-2 rocket, the first of which was unsuccessful, the second of which took place without a payload. Landspace plans to launch three Zhuque-2 rockets in 2024, six in 2025 and 12 in 2026. Undoubtedly, this is a great success for Chinese space science. The Russian Federation is also working on the development of a rocket whose engines run on methane. The carrier being developed under one of the projects, named Amur-LNG, will be able to launch payloads weighing from 9.5 to 12 tons into near-Earth orbits. The first stage of the rocket will be reusable. The methane-powered rocket requires new engines, which are being developed by specialists from a number of organizations. International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association held the XVIIth International Conference "Multimodal Transports of Dangerous Goods. Fuel of the Future.The Way to the Sustainable Development", where the issues of methane application as a fuel were discussed. The participants of the conference noted the promising potential of this energy carrier. Discussion of methane application opportunities in various fields (space, transport, energy) on an equal footing with other promising fuels will be continued at the next conference "Fuel of the Future - the Way to the Sustainable Development" to be held on June 4, 2024. | |
Is vodka dangerous good? | 08.12.2023 |
|
Many household products, which have everyday use, may pose a danger to humans and under certain specific conditions they are to be considered as dangerous cargoes, which should packaged and transported in compliance with international and national regulations for the carriage of dangerous goods by various means of transportation. At the same time, some international rules, such as those annexed to the Agreement on the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR), are applied as national regulations. On New Year´┐Ż Eve, the volume of transportation of alcohol-containing products increases. Often such products are carried in containers on board sea and river vessels. Shippers and transportation companies, whose employees are not familiar with the rules of transportation of dangerous goods, have difficulties in determining whether an alcohol-containing product is a hazardous cargo or not. In this regard, in cases where the rules of transportation do not consider such a product as dangerous goods, it is presented for transportation as dangerous goods, and vice versa, in cases where an alcohol-containing product is defined by the regulations as dangerous good, it is presented for transportation and transported as non-dangerous. In the lists of dangerous goods of the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods and the rules based on them, formulated in the International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code (IMDG Code), ADR and others alcohol-containing products are listed under UN number 3065: ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES containing more than 70% alcohol by volume, Hazard Class 3 (flammable liquids), Packing Group II (substances presenting medium danger) and ALCOHOLIC beverages containing more than 24% but not more than 70% alcohol by volume, Hazard Class 3 (flammable liquids), Packing Group III (substances presenting low danger). Special provision 146 applies to beverages assigned to packaging group II, special provisions 144, 145 and 247 apply to beverages assigned to packaging group III. The special provision 144 provides: An aqueous solution containing not more than 24% alcohol by volume is not subject to these Regulations. The special provision 145 specifies that other than for air transport, alcoholic beverages of packing group III, when carried in receptacles of 250 liters or less, are not subject to these Regulations. In the special provision 146 it is stated: Other than for air and sea transport, alcoholic beverages of packing group II, when carried in receptacles of 5 liters or less, are not subject to these Regulations. The special provision 247 applies to the transportation of alcoholic beverages as part of a manufacturing process. Thus, if we talk about vodka containing 40% alcohol by volume and placed in ordinary consumer containers, then on the basis of Special Provision 145 it is not subject to the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, unlike alcohol. However, this does not exclude the need for knowledge and experience in handling such a popular product and compliance with its packaging, storage and handling requirements. Although vodka is not classified as dangerous good in terms of international regulations, this product requires special attention in terms of its origin, cleanliness of packaging and use to ensure that it is not harmful to health. UN ECOSOC experts on the transport of dangerous goods pay special attention to the fact that special training in the field of handling of dangerous goods should be provided not only to employees of specialized companies (shippers, carriers, transport and logistics companies), but also to representatives of those companies that deliver household products to consumers. The International Staff Training Center conducts regular training for employees of such companies, including those working on e-commerce platforms. The training will significantly improve safety when delivering hazardous products to consumers. | |
| 07.12.2023 | |

Mr. Arsenio Antonio Dominguez Velasco has been confirmed as the Secretary-General of the International Maritime Organization (IMO). The IMO Assembly 1 unanimously approved (30 November) the decision of the IMO Council2 at its 129th session (C129) to appoint him to the role. Dominguez Velasco will take up the office of Secretary-General on January 1, 2024, for an initial term of four years, ending on December 31, 2027. Arsenio Antonio Dominguez Velasco is the Organization's 10th elected Secretary-General. He is currently Director of IMO's Marine Environment Protection Committee since January 2022, joined the IMO Secretariat in 2017 as Chief of Staff to the Secretary-General, Kitack Lim. In 2020 Arsenio Antonio Dominguez Velasco was appointed as Director of the IMO Administrative Division. From his biography it is known that Mr. Dominguez Velasco graduated in 1988 with a Bachelor of Science degree from the Fermin Naudeu Institute in Panama before going on to study Naval Architecture at the University of Veracruz, Mexico, from where he graduated in 1995. Mr. Dominguez Velasco also holds an MBA from the University of Hull, and a Certificate of Higher Education in International Law and European Politics from Birkbeck University (UK). His maritime career began in 1996 as a port engineer at Armadores del Caribe in Panama, then becoming a Drydock Assistant Manager at Braswell Shipyard. Mr. Dominguez Velasco represented Panama in a variety of roles at the organization and was appointed as Panama Permanent Representative to IMO between 2014 and 2017. Mr. Dominguez Velasco chaired IMO's Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC), and in 2015 he chaired the Technical Committee of the 25th session of the IMO Assembly. He has also chaired the Maritime Security ´┐Ż Piracy and Armed Robbery Working Group under the auspices of the IMO's Maritime Safety Committee. Addressing the Assembly, where he was confirmed as the IMO Secretary-General Mr. Dominguez Velasco said:"You have my full commitment to build on the great work that has been done by my predecessors, taking what is already a significant and influential organization, to be an institution that will thrive in delivering its full agenda, from safety to decarbonization, from digitalization to the human element; an International Maritime Organization that not only looks towards the future, but does more in embracing change, diversity, inclusion and transparency; one that is dedicated to its people, from all the very professional staff that form the IMO Secretariat, to our seafarers worldwide and perhaps most importantly, a dedication to the younger generations, the ones we are obliged to hand over to, to hand over a planet that is a better place to live in." Source: IMO IDGCA congratulates Mr. Arsenio Antonio Dominguez Velasco on his confirmation as Secretary General of the International Maritime Organization and wishes him a success in his work in this post. 1. The IMO Assembly is the highest governing body of the Organization. It is composed of 40 leading maritime nations and meets every two years in ordinary session. The Assembly is responsible for approving the program of work, voting on the budget and determining the financial arrangements of the Organization. The Assembly also elects the Council. 2. The IMO Council is elected by the Assembly for a two-year term beginning after each ordinary session of the Assembly. The Council is the executive body of IMO and is responsible for overseeing the work of the Organization. Countries are divided into categories A (10 States having the greatest interest in the provision of international maritime transport), B (10 States having the greatest interest in international maritime trade) and C (20 States not elected under (a) or (b) above that have special interests in maritime transport or shipping and whose election to the Council would ensure representation of all major geographical regions of the world). | |
Composite materials are making their way | 01.12.2023 |

Composite materials are being used more and more in the manufacture of equipment for the transport of dangerous goods. A new Chapter 6.9 has been added to the 22nd edition of the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, which sets out the requirements for portable tanks made of composite materials. The latest session of the UN ECOSOC Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, which concluded in Geneva on December 1, approved a new section of the Model Regulations, 6.9.3, dealing with service equipment for portable tanks made of composite materials and composite (metal-composite) materials. New testing requirements for composite materials have also been developed and will be included in the UN Manual of Tests and Criteria. The initiator of proposals on this application of composite materials is the Russian Federation. From the side of the Russian Federation there was also a proposal to expand the range of dangerous goods that can be transported in portable tanks made of composite materials, in particular, we are talking about goods of the 2nd class of hazard (gases). There are both positive and negative reactions on the part of UN experts. It is clear that gases are usually transported either under high pressure or in a liquefied state, and the practice of using composite portable tanks for gases is very limited. It is interesting to note that back in the late 90's the company Metallocomposite LLC, headed by the General Director Dmitry Grigoriev, developed a project of a tank container made of composite materials for transportation of propane-butane mixture with the maximum working pressure of 19 bar, manufactured a prototype and tested it. The design documentation was approved by the Russian Maritime Register of Shipping. The base for the material and the product itself was one of the institutes in Khotkovo under the technical guidance of professor Alexander Ermolenko. Approximately at the same time on behalf of the Russian Federation the proposal was submitted to the International Maritime Organization (IMO) on development of the corresponding requirements and rules for their introduction into the International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code (IMDGC) for the purpose of provision of transportation of dangerous goods by sea in portable tanks made of composite materials. At the session of the IMO Sub-Committee on the Transport of Dangerous Goods and Containers the developers of the new type of composite tank container demonstrated their developments, which received general approval of this direction. Unfortunately, due to the difficult transition period in the Russian Federation, after testing of the tank-container sample, the work was stopped due to the lack of funds of the company Metallocomposite Ltd. Many years later these developments were continued and approved at the UN and IMO level. Now the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology has become the holder of this direction. The IDGCA experts believe that when developing the requirements for portable tanks made of composite materials for transporting gases, both pressurized and liquefied, the experience and practice of manufacturing a tank container made of composite materials of the 90s will be taken into account, including the results of tests of the world's first sample of such a container. The IDGCA experts actively participate in the activity of all the working groups on development of requirements to composite materials and designs of products from them and, probably, will take part in development of new rules, as some of the experts of the Association participated in development of the first unique tank container in the 90s. It is very unfortunate that the new owners of the rights to manufacture portable tanks from composite materials do not remember those people, designers and businessmen who in the 90s invested their funds, forces, experience and years of life in the creation of this equipment. | |
Another incident on the US railways | 24.11.2023 |
|
According to a number of media reports, 16 wagons with molten sulphur derailed in the US state of Kentucky, with two wagons damaged, resulting in the release of the substance and subsequent fire. According to the UN classification, MOLTEN SULPHUR has UN number 2448, Hazard class 4.1 - flammable solids, self-reactive substances, solid desensitized explosives and polymerizing substances. The self-ignition temperature is 190´┐ŻC. During thermal destruction sulphur dioxide is emitted, which irritates respiratory organs and mucous membranes of eyes, causes bronchial spasm, at high concentrations suffocation, pulmonary oedema, lethal outcome are possible. According to the Globally Harmonized System of Classification of Hazards and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) classification, this substance is flammable (GHS Class 2), skin irritating/irritating (GHS Class 2), causing serious eye injury/irritation (GHS Class 2, Division 2B), selective toxicity to target organs and/or systems with repeated or prolonged exposure (GHS Class 2). If in relation to molten sulphur the hazardous properties of this substance are described quite specifically, the same cannot be said about sulphur in the solid state (UN number 1350, Hazard Division 4.1). It would seem that everything is obvious here: sulphur is a hazardous substance. But special provision 242 of the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods states the following: Sulphur is not subject to these Regulations when it has been formed to a specific shape (e.g. prills, granules, pellets, pastilles or flakes). Similar provisions are found in sectoral regulations governing the carriage of dangerous goods by different modes of transport. The International Code of Carriage of Bulk Cargoes by Sea also lists sulphur as "dangerous" and "non-dangerous". After an in-depth analysis of the rules, IDGCA plans to send a proposal to the UN Sub-Committee of Experts. | |
Training Of The Loading Masters For Marine Oil Terminals | 21.11.2023 |

In the period from November 27 till December 1, 2023 at the premises of ISTC training courses for experts working in marine oil loading terminals with professional qualifications in ‛Marine Oil Terminal Loading Master´┐Ż. Course program is based on ´┐ŻSafety Guidelines and Good Industry Practices for Oil Terminals´┐Ż developed by UN with the purpose to improve the safety in oil terminals. The subjects on ensuring the safety in marine oil terminals, specified by national legislation, provisions of international conventions, codes, agreements and recommendations, risk assessment procedure in tank vessel ´┐Ż terminal interaction, safety requirements for carrying out handling mooring lines and cargo handling and other issues are included in the course program. Similar training courses for experts working in marine LNG terminals with professional qualifications in ‛Marine LNG Terminal Loading Master´┐Ż will take place in the period from January 22 till January 26, 2024. The availability of qualified professionals is the guarantee for successful and safe terminal operation. | |
63RDSESSION OF UN SUB-COMMITTEE OF EXPERTS ON THE TRANSPORT OF DANGEROUS GOODS | 17.11.2023 |
 
63rd session of ECOSOC Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, plenary meeting, will be held in Geneva, Switzerland, from November 27 till December 6, while from December 6 till 8 a meeting of experts in GHS (Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals) will took place. The International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association represented by the Director General Mikhail Ognev will take part in the work of UN Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. The meeting will be conducted according to the program and official and informal documents submitted by countries and non-governmental organizations. During the session meetings of working and informal groups will be held. In particular, meeting of informal working group on FRP service equipment is planned. In course of the session lively discussion on subjects of carriage of certain dangerous goods (particularly hydrogen peroxide) in composite IBC containers. In the preceding session Mikhail Ognev came up with the proposal to make amendments in the UN Model Regulations concerning manufacturing and use of IBC containers and service equipment, with which the composite IBC are fitted. Problems, related to handling and operation of IBC and service equipment, are also raised by a representative of Netherlands in the information document ? UN/SCETDG/63/INF.9. Practice of carriage of dangerous goods in IBC containers gives evidence of frequent emergencies in the course of carriage of dangerous goods in given IBC type, which is used very widely in the world while transporting dangerous cargoes. It is possible that in the session a question of training for experts and responsible persons, which prepare transport documents and cargo for dispatch. The International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association, comprising the International Staff Training Centre, during already more than 20 years trains specialists in the sphere of carriage of dangerous goods at a high professional level and hands over practical skills of work with dangerous goods through the training and preparation of transport documents. The last group of experts was successfully attested for the title of dangerous goods safety adviser on November 17. Next training and attestation of dangerous goods safety advisers are scheduled in December this year. | |
ARCTIC: THE PRESENT AND THE FUTURE | 09.11.2023 |
 
On December 7-8 in Saint-Petersburg XIII International Forum ‛Arctic: Present and Future´┐Ż will be held. Reclaiming of Northern Sea Route and Arctic was considerably predestined by production and processing of hydrocarbons. LNG terminals and oil terminals are actively built and developed in Arctic zone, without which it is impossible to service marine vessels, gas carriers, chemical carriers providing carriage of cargoes in the Arctic. Construction and operation of marine terminals, floating, stationary and submersible, in the Arctic are involved with the great environment pollution risk for Arctic coastal waters. World statistics show that main emergencies and incidents happen in ‛ship-to-shore´┐Ż interaction in the course of cargo handling operations. One of key factors for reduction risk of potential accidents, besides fitting with up-to-date equipment and use of modern control systems, is the staff training. At the invitation of the Forum Organizing Committee executives of International Dangerous Goods & Containers Association will take part in the event. A presentation is planned. | |
New LNG vessels | 03.11.2023 |
 
XIInd Peterburg International Gas Forum (PMFG-2023) is held in Saint-Petersburg. This is one of key events for world gas industry. IDGCA head and experts take part in the forum work. In Expoforum exhibition platforms, where PMFG-2023 take place, the wide range of options for gas industry is displayed, exhibitions, conferences, sessions are held, round-table discussions are led, agreements significant for Russian and foreign enterprises are signed. The forum final totals will be carefully considered by IDGCA experts and we will inform you of the work results later, but for the present it is worth pointing out the information heard at the event that concerns advanced developments in the transport industry, which are based on the use of liquefied natural gas (LNG). In this respect the report of ‛Gazprom SPG Technologies Ltd´┐Ż relating to plans for design and construction of bunkering barge and pushboat on LNG in the next future is of special interest. With the consideration of current developments in LNG technologies, including trends in maritime transport the training programs for Loading masters and LNG Marine Terminal Operators were developed and successfully implemented in IDGCA in Association subsidiary ´┐Ż International Staff Training Centre. In the programs the most recent requirements of international conventions, regulations and standards applied in the sphere of LNG carriage and storage as well as carrying out cargo handling and bunkering operations as regards this advanced energy carrier, are taken into account. Graduates, passed training and examination, get internationally recognized certificates. | |
Maritime transports of dangerous goods in high-capacity containers | 27.10.2023 |
 
Matters of prevention for emergency situations arising in the course of carriage of cargoes in containers in sea ships always were in the spotlight of International Maritime Organization (IMO). In IMO headquarters in London on October 23-26 the session of expert group for Formal Safety Assessment (FSA), which concerned range of problems of fire detection and fighting in cargo holds and cargo decks of container ships. During the session results of investigation under the name of "CARGOSAFE", which was carried out at the commission of European maritime Safety Agency (EMSA), were considered. The fire safety problem was examined in terms of risk assessment taking into account two aspects:
According to results of the work done, as expected by FSA experts a draft of amendments to Chapter II-2 of International Convention for Safety of Life at Sea SOLAS 74 and Fire Safety System Code (FSS) based on suggested options for risk assessment and other materials of "CARGOSAFE" investigation will be developed. Analysing the emergency situations related to carriage of dangerous goods in containers the IDGCA experts came to the conclusion that a cause for fire often is improper processing of dangerous cargo for the carriage by sea and improper execution of transport documents and sometimes properties of dangerous good, which are unaccounted for during the transport. International Dangerous Goods & Containers Association significantly contributed to solving the problem of ensuring the fire safety in the course of container carriages. In co-operation with specialists of a number of leading engineering organizations IDGCA developed the concept and technology solutions for automatic fire extinguishing within cargo transport units. But regardless of development need in new equipment types for carriage of dangerous goods IDGCA supposes that the most effective way for prevention of emergency situations is proper training of specialists, therefore IDGCA draws particular attention to development and special training program of experts. ISTC,which was 20 years this year, already trained more than 3000 dangerous goods' advisers in all corners of Russia | |
Interim safety guidelines for ships using hydrogen and ammonia as marine fuel | 13.10.2023 |

Sub-Committee on Carriage of Cargoes and Containers of International Maritime Organization (IMO) in the session held on September 20-29 considered among other issues a draft of interim safety guidelines for ships using hydrogen and ammonia as marine fuel. Taking into account the necessity of exigent providing of administrations, ship-owners and industry in whole with guidelines of this sort the Sub-Committee took decision on convening of intersession working group in a period from September 9 to 13, 2024 (subject to adoption by Maritime Safety Committee (MSC) in the 108th session and approval by IMO Council) for finalization of guidelines. If time permits, it will be proposed to the working group to continue the development of draft of interim guidelines for ships using low-flashpoint fuel. The Sub-Committee also approved the draft of MSC Circular on Interim guidelines for using liquefied petroleum gas as fuel. The Sub-Committee decisions proved the importance of IDGCA work on search for solutions in the field of alternate fuels, including marine fuel, which were discussed at the XVIIth International conference ´┐ŻMultimodal Transports of Dangerous Goods. Fuel of the Future. Way to the Sustainable Development´┐Ż held in May, 2023 (´┐ŻThe Conference was organized at the high professional level´┐Ż). Next year IDGCA plans to conduct the new conference at the end of May - beginning of June, where the problems of transition to new fuel sorts will be raised again. | |
Plans for prevention and response to spill of oil and petroleum products | 02.10.2023 |
|
For which objects Plans for prevention and response to spill of oil and petroleum products should be developed and approved? In compliance with requirements of RF Government Decree of 31.12.2020 ? 2451 ´┐ŻOn approval of Regulations for organization of measures for prevention and response of spill of oil and petroleum products in the territory of the Russian Federation, except for internal marine waters of the Russian Federation and territorial sea of the Russian Federation as well as on annulling of certain acts of Russian Federation Government Acts", for determination of objects, the operation of which is allowed in the presence of these Plans, the criteria are as follows: ?) maximum design volume of spill of oil and petroleum products for objects, situated (operated) in surface water sources (including their water protection zones) other than seas and their various parts, - 0.5 tons and more; b) maximum design volume of spill of oil and petroleum products for objects, placed in land part of Russian Federation territory - 3 tons and more. While providing training for staff of oil terminals (heads, loading masters, loading operators and other personnel categories, working in the terminals) the International Staff Training Centre also offers services of development of Plans for prevention and response to spill of oil and petroleum products. Besides the development by itself the methodical support of procedure for approval of such plans is provided. The procedure is quite difficult and planning and carrying of comprehensive training exercises for demonstration of emergency preparedness of operating organization for measures of containment and cleanup of maximum design volume of spill of oil and petroleum products plays the most important role. Just according to results of these training exercises the commission for confirmation of emergency preparedness of operating organization for measures of containment and cleanup of maximum design volume of spill of oil and petroleum products, comprising representatives of federal executive authorities as well as public authorities of subjects of the Russian Federation and local self-government bodies, in territories of which an object of operating organization is situated and chairman of the commission is a representative of territorial authority of Ministry of the Russian Federation for Civil Defense, Emergencies and Elimination of Consequences of Natural Disasters in corresponding subject of the Russian Federation, make an appropriate judgment. If you contact the ISTC or IDGCA, you will receive the necessary advice. | |
To the attention of oil companies | 25.09.2023 |
|
In Saint-Petersburg at the address: 35A Marshala Govorova str., of. 440, from October 2 to October 6 in the International Staff Training Centre the training of heads of marine oil terminals will be held. Requirements specified by national legislation for safety ensuring in oil marine terminals, provisions of international conventions, codes, agreements and recommendations, risk assessment procedures for interaction between tank vessel and terminal, safety requirements for carrying of linehandling and cargo operations and other issues will be studied in the courses. In the course of training the trainees will have the opportunity of visit to one of marine oil terminal. According to the training results the participants will obtain certificate of skill enhancement and international certificates issued by the International Dangerous Goods & Containers Association. The training program may be interesting for chiefs of marine oil terminals as well as for heads of marine LNG terminals. Representatives of leading oil companies of Russia will take part in the training. Teachers will hand over unique hands-on experience of safe work in marine oil and gas terminals to the trainees. | |
Explosion of tank car with perchloric acid in USA. What are the conclusions? | 15.09.2023 |
|
According to a number of mass media in American state Nebraska a car with perchloric acid, followed in railroad train, was exploded.Perchloric acid (chemical formula HClO4) is used in some industry fields, including in production of rocket-engine propellant. This substance is characterized by high corrosivity, reactivity, is strong oxidizer and moreover it is incompatible with some substances because of its explosion risk when in contact. In the Dangerous Goods List of the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods this substance depending on the concentration in the solution, is described two times:
When analysing the accident we cannot fail to note that the union of railroad workers and employees of this country considers insufficient staff qualifications as one of primary reasons for accidents, which became frequent, in the course of cargo transportation by rail in USA. In Russian railroads personnel training and certification, involved in the carriage of dangerous goods, are governed by a number of regulatory documents. The same cannot be said of maritime and inland water transport of Russia, since requirements to training of persons, responsible for carrying out of such activities for the purposes disappeared even from provisions concerning licensing of carriage of dangerous goods and handling operations. ISTC holds on a regular basis the training of persons, responsible for work with dangerous goods. The training program includes the analysis of accidents with dangerous goods. | |
The 9th session of the International Maritime Organization (IMO) Sub-Committee on Carriage of Cargoes and Containers (CCC) on September 20-29 | 12.09.2023 |
|
The 9th session of the International Maritime Organization (IMO) Sub-Committee on Carriage of Cargoes and Containers (CCC), which deals with the carriage of packaged dangerous goods, solid bulk cargoes, bulk gas cargoes and containers, will meet in London on September 20-29. The key issue for the IMO CCC Sub-Committee Session will be the problem of safe use of alternative fuel types by ships.The following questions will be considered:
Amendments to the IGC Code to include ‛Safety provisions for the safe use of LPG cargo as fuel´┐Ż, The new safety requirements are concerned with use of low flashpoint oil fuels, which will have significant costs for shipowners, in particular, for those who is forced to adapt the available ships for new fuel standards and types with low carbon content. | |
Acid spill in Kazakhstan | 30.08.2023 |

According to the information of website zakon.kz on August 28 in the Ekubastuz-2 railway station leak of sulphuric acid from rail tank car was developed. The total weight of the cargo, carried in two rail tank cars, accounts for 78.3 tons. Local authorities took measures for containment of the accident and emergency treatment operations. In particular, bunding of spill site with sand and lime carbonate was made, two rail tank cars for transfer of the product to them were delivered.SULPHURIC ACID, containing more than 51% of acid, is dangerous good of Hazard class 8 (corrosive substances), UN 1830. In compliance with Regulations of carriage of dangerous goods by rail in CIS countries in case of carriage of the substance requires the protective distance ‛0-0-1´┐Ż (leading digit ´┐Ż from lead locomotive, second-position digit ´┐Ż from bank locomotive, third-position digit ´┐Ż from cars with people). In cases of accidents with the substance the emergency card 801 shall be applied, according to which to neutralize the substance it is necessary to take the following actions:
| |
Liquefied gas from Saint-Petersburg will go via the Northern Sea Route | 26.08.2023 |
|
On August 14 the tank vessel ‛Velikiy Novgorod´┐Ż fully loaded headed for towards the Northern Sea Route. Offloading of liquefied natural gas (LNG) was made on the terminal LNG Facility KSPG Portovaya, which is located in Vyborg District of Leningrad Region on North-East coast of Gulf of Finland, in 60 km from Vyborg town and 7 km from the border with Finland. The terminal operator is ‛Gazprom SPG Portovaya´┐Ż Ltd. It is pleasant to note that among responsible employees of cargo complex ‛Gazprom SPG Portovaya´┐Ż Ltd. loading masters work, which were trained in the International Staff Training Centre and obtained the international qualification Terminal Loading Master. Training program for loading masters, working in the terminal of offloading of liquefied hydrogen gas was developed by the ISTC in cooperation with experts of International Dangerous Goods & Containers Association (NP ‛IDGCA´┐Ż) and comprise the study of international conventions, regulations and standards as applicable to LNG terminals. For the first time international ISO standards on cryogenics were studied, the translation of which was made by experts of IDGCA on the assignment of Russian Institute for Standardization. Next training courses for specialists on the program Terminal Loading Master will be held on October 2-6, 2023, in the ISTC. | |
Tragedy in Makhachkala | 17.08.2023 |

On August 14, 2023, our country was floored by tragic report on explosion in Makhachkala. The explosion claimed the lives of 35 persons, 65 people remain in hospitals. Serious violations were already detected in the gasoline station, a criminal case was opened under the article ´┐ŻRendering of services falling short of safety requirements for consumers´┐Ż life or health that entailed death of two or more people through negligence´┐Ż. According to information of newspaper ‛Kommersant´┐Ż and initial findings of the investigation a fire took place in the service station building neighbouring to the fuel filling station, subsequently the fire spread to an adjacent premise, in which according to the preliminary information ammonium nitrate in bags was, whereafter an explosion occurred. It is perplexing why ammonium nitrate was near the fuel filling station. If this is ammonium nitrate UN 1942, hazard class 5.1 ´┐Ż Oxidizing substances, the substance is classified as high consequence dangerous good ´┐Ż goods that may be used not only for intended purpose as a fertilizer, but also for terrorism purposes. Accidents, caused by handling of this substance without the knowledge, are numerous, including recent the largest disaster accidents the explosion in Beirut port August 4, 2020. The training of responsible persons as well as any other experts, whose activity is immediately associated with carriage, storage, loading and unloading of dangerous goods, is essential measure for prevention of accidents and incidents. In particular, it is oddly enough that in the new RF Government Decree ´┐Ż 2111 of 30.11.2021 on licensing of cargo-handling operations in sea and river ports there not requirements to training of experts on dangerous goods, although all the international conventions, agreements and regulations require the training of all the persons, whose work is associated with dangerous goods. Competent authorities, onto which Ministry of Transport shifts more and more responsibility and functions of control over conducting activities, associated with carriage of dangerous goods, can hardly ensure the safety without participants of transportation process, having sufficient knowledge and well qualified for work with dangerous goods. The International Dangerous Goods & Containers Association expresses the deepest condolences to families of whose involved in this ghastly accident. | |
Negligent performance of duties, confluence of circumstances or diversion, what led to the explosion in a grain elevator? | 09.08.2023 |

According to CNN Turk report and a number of news media of August 7, 2023, near Turkish seaport Derince in Kocaeli province an explosion took place. According the information of Anadolu agency the explosion occurred in the coastal area of the region around 14:40 in the grain elevator at the time of loading of ship with grain. The Kocaeli Province Governor Seddar Yavuz declared that there are injured persons from the incident. Search and rescue teams were sent to the explosion site. CNN Turk reported of five people injured. According to the latest figures there were not less than 13 casualties, one of them died in a hospital. 13 of 16 port grain elevators were damaged. Explosion shock wave did not touch the port container area. Proximate houses received minor damages, added Mayor of Derince. Now services discharge the grain from all the elevators. Zeki Ayg´┐Żn noted that experts will check whether somebody could be at the moment of explosion inside the grain elevators. Derince is situated in Turkish province Kocaeli at 95 km from Istanbul. The port is in the Gulf of Izmit in Marmara sea. As Turkish news media say, the explosion was felt in nearbu town G´┐Żlc´┐Żk. There are several versions of the explosion causes. Director General of Turkey Grains Board, that is the owner of the elevators, Ahmet Guldap announced that the reason of explosion was the detonation of grain dust in the elevator. According to another version in the TASS report Turkish leadership do not rule out the possibility of diversion as the explosion cause. Negligence in the work with grain is taken as one of potential reasons, though the grain in itself is not classified as dangerous good according to the UN Dangerous Goods List, except for seed cake and other special products, which are classified as dangerous goods in compliance with the UN Model Regulations. In any case there are internal regulations, prescribing safe working procedures for elevators, there may be a violation of these procedures and it was the cause for explosion. | |
IMO intends to collect maritime personnel´┐Żs views on the application of the International Safety Management Code (ISM Code) on board ships | 02.08.2023 |

The International Maritime Organization proposes staff of sea transport to fill in the online-questionnaire within the framework of comprehensive study on effective implementation of the International Safety Management Code (ISM Code). The ISM Code is international standard for the safe management and operation of ships and for pollution prevention. It requires shipping companies to carefully consider their management structure and the responsibilities and authorities of those involved in the operation of their ships from the safety and environmental protection point of view. The ISM Code is mandatory since 1998. IMO announced that those wishing to participate in this survey can do it until September, 30. The study findings will be submitted to the Maritime Safety Committee in the course of the 108th session, which will be held on May, 15-24, 2024. Such a decision of the International Maritime Organization is absolutely correct, since the putting into practice of the Code in some organizations resulted not in improving the safety management on board ships at sea, but to development of numerous documented procedures, the compliance with the procedure required much time and distracted from carrying out practical measures for ensuring the safety on the part of the crew. Moreover, the Code was additional instrument, the observance of which is supervised by classification societies through the Safety Management System certification. Some provisions of the Code are based on ISO 9000 standards, which have not direct relation to the safety management on board ships at sea. Assessment of effective implementation of ISM Code and the practical use by maritime personnel will promote its further reasoned implementation. ´┐Żlassification societies and inspection bodies render the services to shipping community for tidy remuneration and in that case additional requirements may arise on their part to the scope of documentation and operation of safety management system. The Regulations concerning solely safety issues specify requirements to the management system and referred to standards, which have not direct relation to the safety aspects. It may be hoped that after fundamental survey among maritime personnel, which directly implement the ISM Code in the practice, the additional arrangements for improving of the Code and its interpretation will be developed | |
Field Class | 28.07.2023 |

In the period from July 17 to July 20, 2023, training courses at the base of ‛LUKOIL-Nizhegorodnefteorgsynthez´┐Ż Ltd to improve the qualifications of employees of ‛LUKOIL-Nizhegorodnefteorgsynthez´┐Ż on the topic: ´┐ŻCarriage of dangerous goods by rail´┐Ż were held. The course program was developed with due account for internal technical regulations of the company and legislation of the RF. Perfect organization of the courses enabled ISTC teachers to carry out fully the program and convey the necessary information to the maximum extent to trainees. The ISTC activity received a high appraisal. | |
Lithium batteries can be source of fire and cause for loss of ship | 27.07.2023 |
|
According to report of Dutch Broadcasting Foundation (NOS) (Netherlands) in cargo ship Fremantle Highway in the North Sea not far from Ameland the fire broke out. The ship transported 3000 cars from Germany to Egypt. One person was killed and some others were injured, the crew was evacuated, the ship is setting adrift, emergency response group is working. According to preliminary information the fire started from one of twenty five electric vehicles that were on board. There are no information about exactly what kind of power sources (batteries) were used in this electric vehicle, but it is obvious that they can be classed as lithium batteries. Lithium batteries, including installed in transport equipment, are dangerous goods, and in the Dangerous Goods List of International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code (IMDG Code) there are 7 categories of such electric power sources:
IMDG Code establishes rules for sea carriage of every type of lithium batteries, including packing instructions and EmS (Emergency Response Procedures) F-A and S-I. It is necessary to handle lithium batteries, including lithium ion and lithium metal batteries installed in certain equipment with due care. The UN ECOSOC Sub-Committee on the Transport of Dangerous Goods keeps a strong focus on development and improvement of carriage rules for lithium batteries, testing methods and operation safety. At 62nd session of UN ECOSOC Sub-Committee on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, held in the period from July 3 to 7, 2023, the Sub-Committee expressed appreciation to the activity of Informal working group on classification of lithium batteries. | |
Non-Dangerous Sulphur Does Not Exist | 26.07.2023 |

According to report of news agency ‛RZN.info. Ryazan´┐Ż at the railway station in Sasovo (Ryazan Region) a combustion of sulphur in railway cars took place. As EMERCOM of Russia comments, the fire begun on July 26 at 7:25, the spread of fire was contained at 8:20 in the area of 80 sq. m, at 8.57 was extinguished. From nearest houses 119 persons were evacuated, there were no injuries. The IDGCA experts note that sulphur is the special type of cargo, which may be classified as both dangerous and non-dangerous good. The point is that in compliance with the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods (further ´┐Ż the UN Model Regulations) sulphur has the number UN 1350, subsidiary risk 4.1 (flammable solids, self-reactive substances, solid desensitized explosives and polymerizing substances). Any persons who deals with sulphur not only at production site and in the transport, but also at home (for example, uses sulphur candles for eliminating of pests), do not have doubts in hazardous properties of the present substance. By the way, apart from the fact that sulphur burns with release of toxic gases, actively reacts with strong oxidizing substances, during carriage and handling it forms the dust, which is in the air has explosion risk. Nevertheless, in the Chapter 3.3 of the same UN Model Regulations the special provision 242 is provided, which states: Sulphur is not subject to these Regulations when it has been formed to a specific shape (e.g. prills, granules, pellets, pastilles or flakes). The same provision can be found in rules for the carriage of dangerous goods by all the modes of transport, for which the UN Model Regulations are basic. There is also the same interpretation (sulphur can be ´┐Żhazardous´┐Ż and ´┐Żnonhazardous´┐Ż) in the International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargoes Code (IMSBC Code). The IDGCA experts believe that sulphur in all the cases and at all the stages of its life cycle is hazardous substance. | |
Training For ADN experts | 25.07.2023 |
|
On August 7-10 in the International Staff Training Centre ADN Basic courses on the transport of dangerous goods by inland waterways in accordance with requirements of European Agreement Concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Inland Waterways (ADN) will be held. The training is conducted by instructors with unique practical experience in working on ships and river vessels as captains and chief mechanics, as well as teachers with extensive experience in supervisory bodies and classification societies. After the training the participants will have knowledge of ADN basic provisions, hazard classes of dangerous goods, the main properties, common types of hazards, posed by substances of various classes, escorting rules for dangerous goods, content and principal technical characteristics of equipment used in conducting loading and unloading operations with dangerous goods, forms and content of transportation documents for dangerous goods, prevention methods and procedures for emergency situations when working with dangerous goods, application rules for fire-fighting equipment and use of personal protective equipment, first aid to persons injured by incidents with dangerous goods. On completion of the course the participants will get state-recognized documents of skill improvement and internationally recognized certificates of ADN expert. | |
Joint Meeting of Experts on the Regulations annexed to the European Agreement Concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Inland Waterways (ADN) | 25.07.2023 |

On August, 21-25, 2023 in Geneva (Switzerland), in the Palais des Nations 42nd session of Working Party on the Transport of Dangerous Goods of ECOSOC Inland Transport Committee, Joint Meeting of Experts on the Regulations annexed to ADN will take place. In the provisional agenda the following questions are planned to consider:
| |
ADN Courses in the International Staff Training Centre | 21.07.2023 |
|
On August 7-10 in the International Staff Training Centre ADN Basic courses on the transport of dangerous goods by inland waterways in accordance with requirements of the European Agreement Concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Inland Waterways (ADN) will be held. Applications can be sent to the e-mail:istc@idgca.org | |
The UN model regulations is result of collective intelligence of experts from various countries | 21.07.2023 |
|
On July 3-7, 2023, 62nd session of the UN Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods was held in Geneva (Switzerland). In the course of session the following questions were discussed: testing of explosives, review of packaging and transport requirements of explosives, requirements to testing and transport of lithium and sodium-ion batteries, carriage of gases, global recognition of UN and non-United Nations pressure receptacles, consideration of miscellaneous proposals for amendments to the Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods concerning marking and labeling, packagings, use of portable tanks, dangerous goods safety training, issues relating to the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS): testing of oxidizing substances. Along with other proposals and documents results of work of informal working group on fibre reinforced plastics (FRP) service equipment for portable tanks, which was organized at the suggestion of the Russian Federation and supported by Sub-Committee experts, were considered. The informal working group worked between sessions through correspondence and communication in Zoom and continued the work during the session. The Head of the informal working group Ivan Sergeichev, RF representative, at the plenary session acquainted the participants with results of work as the draft of New Chapter 6.9.3 for introduction to the UN Model Regulations. Experts of the IDGCA, from Russia, Germany, France and Poland were actively involved in the activity of informal working group. In particular, Mikhail Ognev, Director General of the IDGCA, made a proposal concerning requirements to the quality ensuring system in designing, testing and manufacturing of service equipment of composite materials. In many parts of the UN Model Regulations requirements to quality system were not clearly defined and understanding of these requirements was problematic for manufacturers of products subject to UN Model Regulations, IMDG, ADR, AND relating to a carriage of dangerous goods. Different interpretations of the term ‛quality system´┐Ż often led to unfounded requests on the part of inspection bodies, which performed functions of confirmation of manufacturers´┐Ż compliance. The IDGCA experts proposed the brief formulation, which defined the quality system and established the requirements. The IDGCA also prepared for the session official document ST/SG/AC.10/C.3/2023/29 and unofficial document UN/SCETDG/62/INF.38, that concerned requirements of the UN Model Regulations to intermediate bulk containers (IBC), intended for carriage of dangerous goods, including cargoes of 8 Hazard class. Intermediate bulk containers (IBC), so called cubes, are popular enough in the carriage of dangerous goods in multimodal transports in cargo transport units. IBC are composite (compound) containers, consisting of inner receptacle, made of rigid plastic and outer casing, enclosing the receptacle. In the opinion of the IDGCA experts, lack of sufficient requirements in the UN Model Regulations to design and testing of service equipment as well as bottom discharge (and, as a consequence, a possibility of setting of valves in IBC that have improper quality) may lead to accidents. The 62nd session of Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods is the first session after coronavirus pandemic. In addition to formal communication experts had a possibility to interact with each other in the informal meeting while having dinner in one of Geneva restaurants. The session was successful. The next 63rd session of Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods will take place on November 27 ´┐Ż December 6, 2023. | |
New 23rd Revised Edition of the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods | 19.07.2023 |

A new revised edition of the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods in English, addressed by the UN Secretariat to the IDGCA, came to the library of International Dangerous Goods & Containers Association. In the preparation of different expert reports as well as in the course of training of experts IDGCA and ISTC always use exclusively updated documents. In such a case they have to refer to an edition in English, as a text in Russian sometimes differs from a text of principal language, which is working for experts of various countries. The IDGCA thanked the UN Secretariat for sending of the UN Model Regulations to the Association. | |
Yet another victims of confined spaces | 30.06.2023 |
 
According to the information of agency ‛Kazanreporter´┐Ż in the territory of oil producing headquarter ‛Elkhovneft´┐Ż of PAO ‛Tatneft´┐Ż in Zainsk Region an explosion of oil tank in reconstruction occurred. In opinion of the IDGCA experts, explosion, which claimed lives of two people took place as a result of gross violations of rules of operations in enclosed spaces. The died company workers were engaged in cleaning of oil tank. A criminal investigation under article ‛Violation of safety rules in explosion hazardous production facilities´┐Ż was open. Regretfully, according to the statistics dozens of people lose their lives each year in enclosed spaces. Most often persons working in confined spaces, which may include stationary and transport oil tanks, bilge premises, closed warehouses, closed cargo transport units such as freight containers etc., as well as heads and supervisors assigning their subordinates to these operations do have neither knowledge nor practical skills in this work. Not all, apparently, know, for example, that common wood material that is in closed space can pose a mortal danger, since as a result of biochemical processes proceeding in the material oxygen concentration in ambient air of working area falls reaching dangerous limit at 16% and below. By the way hazard arises in case of oxygen elevated concentration, that may cause fire breaking-out and rapid propagation. International Maritime Organization (IMO) and United Nations (UN) are very focused on the safety problem of work in confined spaces and developed a set of codes and standards, including e.g., IMO Resolution A.1050(27) ‛Revised Recommendations for Entering Enclosed Spaces Aboard Ships´┐Ż | |
SUMMER COURSES IN THE INTERNATIONAL STAFF TRAINING CENTRE | 26.06.2023 |
|
In a period from July 10 to 14 in the ISTC the next training of experts on safety of the transport of dangerous goods is planned. Training and qualification will be held in the following specialties (categories):
Those wishing to receive the in-person or online training may submit the application. | |
IMO approves Interim LPG and LNG Guidelines | 23.06.2023 |
|
The IMO has taken another step forward in building a regulatory framework for alternative fuels. The 107th session of the Maritime Safety Committee (MSC 107, 31 May to 9 June) approved circular MSC.1/Circ.1666 containing Interim guidelines for the safety of ships using LPG as fuel. These Interim Guidelines will provide an international standard similar to the IGF Code to form the basis for the design, construction and operation of ships using LPG as fuel. IMO has previously developed and approved interim guidelines based on the IGF Code framework for methyl/ethyl alcohols (covering methanol), followed by interim guidelines fuel cell power installations. These guidelines were developed by the IMO´┐Żs Sub-Committee on Carriage of Cargoes and Containers (CCC), which is currently working on interim guidelines for hydrogen and ammonia. MSC 107 also approved MSC.1/Circ1668 containing a Unified interpretation of bunkering manifold arrangements fitted on LNG bunkering ships in the ICG Code. The interpretation clarifies issues related to the risk of leakage and associated safety protection for LNG bunkering vessels, some of which have cargo transfer arrangements in addition to traditional cargo manifolds. (Information source: IMO news of 2023/06/13) Recently the IDGCA ran the conference on alternative fuel types, which was held with success in Peterhof. Key reports will be published in the upcoming issue of journal ‛Dangerous Goods and Containers‛. | |
Collision of two tankers in Lena river and fuel leakage to the water area | 19.06.2023 |

According to TASS information on June 12 near Alekseevka settlement of Kirensk district in the Irkutsk Region there was a collision of TR-900 ‛Erofey Khabarov´┐Ż tanker and TR-901 tanker carrying 832 tons of gasoline. In one of vessels a container with 138 tons of fuel was damaged. The leakage to Lena river water area took place. Presumptively from 60 to 90 tons of gasoline could leak out to the water area. Status of emergency in the Kirensk district and high alert regime in Yakutia were imposed. The Irkutsk Region Governor Igor Kobzev reported that the vessel was navigated by captain´┐Żs mate, since the captain was under influence of alcohol. The vessel escaped from the scene of collision and bolted the Irkutsk Region. The tanker owner reported on this emergency only in an hour, that affected the development of the situation. It is supposed that the vessel could be out-of-repair. Issues of the transport of dangerous goods by inland water transport are subject to the ADN Regulations, which, unfortunately, do not apply on a mandatory basis for inland vessels. The International Staff Training Centre for several years provide its services of ADN expert training, however, they are not in demand in the Russian Federation while key trainees of the courses on ADN programmes are European sailors. It is worth noting that certificates issued by ISTC and IDGCA are accepted by European shipping companies. |
|
Session of ECOSOS Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods (TDG Sub-Committee) | 19.06.2023 |
|
On July, 3-7, 2023 in the Palais des Nations (Geneva, Switzerland) the 62nd Session of TDG Sub-Committee will be held. There are the following issues on the session agenda:
State-members of TDG Sub-Committee and non-governmental organizations, having a consultative status, submitted 30 official working documents for committee consideration. Among them is there the Russian Federation proposal regarding a service equipment for portable tanks and the IDGCA proposal for amendments to Chapter 4.1 of the Model Regulations concerning IBC requirements for the transport of dangerous goods of Hazard Class 8. The official documents are submitted in two months before session and informal documents may be presented for consideration at any time including before starting or during the session. But the priority is given to the official documents. The IDGCA experts plans to become direct participants in the session work in Geneva. | |
ARCTIC: PAST, PRESENT, FUTURE | 09.06.2023 |

Public Television of Russia (OTR) is preparing 15-17 Russian films addressed Arctic past, present and future and Northern Sea Route, which at present got a great incentive to its development from the state. On June 7, 2023, in the office of International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association (further NP "IDGCA") ship captain of OAO "Murmansk Shipping Company" Vladimir Dmitrievsky was interviewed by OTR editors for one of documentals. He worked at the enterprise during 42 years from 1977, of them 30 years as part of the crew personnel (17 years captain of bulk carriers and tankers) and over the last years he held the different leading positions in the OAO "Murmansk Shipping Company" and the major part of his life was associated with Arctic. Vladimir Dmitrievsky was asked and highlighted the issues, which concerned Arctic in the past, how he sees it now and the future of Northern Sea Route as direct witness of Arctic development in 1970-80, then its desolation in 1990-2000 and strong accelerant in its progress in the recent years. He noted that the principal action in the development of Northern Sea Route today is an establishment of Direction of Northern Sea Route last year, which was headed by Deputy General Director of "Rosatom" (ex- First Deputy Minister of Transport of the Russian Federation) Vyacheslav Rooksha having a very profound knowledge of Arctic and, building a qualified team surely under his guidance, Russia will further be accrued by Arctic. It is worthy of note that Vyacheslav Rooksha was the First President of NP "IDGCA" from 2001 till 2004. Questions, posed by the Chief of OTR Service of information broadcasting Svetlana Gubanova, were filled with extensive knowledge of Arctic problems and objectives. At present Vladimir Dmitrievsky work as teacher and expert in the NP "IDGCA". Svetlana Gubanova also interviewed the NP "IDGCA" General Director Mikhail Ognev, which devoted many years of his life to Arctic too, working as chief engineer on ships of Northern Shipping Company, and has an intimate knowledge of the Far North and Antarctic conditions. From 1986 till 1987 Mikhail Ognev took part in the 32nd Soviet Antarctic Expedition and provide jointly with other crew members a failure-free operation of ´┐ŻPavel Korchagin´┐Ż ship. The working environment of Arctic and Antarctic require special skills and knowledges from captains and chief engineers. Every mistake may cost lives of the crew and cause extensive damage to the nature. Mikhail Ognev in his interview brought into focus just that. He said that especially careful attitude to Arctic and Antarctic nature is necessary, since Arctic is not only an unique north route, reservoir of huge oil and gas reserves and other mineral resources, but also extraordinary forest and landscape resources. In arctic rivers and seas unique fish species are found: sturgeon, Siberian white salmon, muksun, starlet, cisco and also abundant fauna. Therefore in spite of technical progress of industry development in Arctic all the arctic rich natural resources as national treasure should be preserved for posterity. Ship captain Vladimir Dmitrievsky and chief engineer Mikhail Ognev share their great professional experience with course participants in the International Staff Training Centre and personnel. | |
The Conference was organized at the high professional level | 02.06.2023 |
|
On May 30 in Peterhof the XVIIth International Conference ‛Multimodal Transports of Dangerous Goods. Fuel of the Future. Way to the Sustainable Development´┐Ż took place. The Conference was held at the high level of organization ´┐Ż such an opinion was expressed by most of the participants, among them were such organizations and companies as GK ‛Rostec´┐Ż, AO ‛Uralcryomash´┐Ż, PAO ‛Geliymash´┐Ż, OOO ‛Arkticheskaya Perevalka´┐Ż, PAO ‛Novatek´┐Ż, FGUP ‛Krylov State Research Centre´┐Ż, ‛RusChemAlliance´┐Ż LLC, OOO ‛Gazprom-neft Shipping´┐Ż, OOO ‛EuroChem Terminal Ust-Luga, AO ‛New Technologies in Transportation´┐Ż, OOO ‛H2 Invest´┐Ż, OOO ‛Fenix´┐Ż (Port Bronka), ZAO ‛TK ‛Chempack´┐Ż, OAO ‛Lukoil-NN´┐Ż, Federal State Budgetary Institution ‛Russian Standardization Institute´┐Ż and many more. In spite of the subjects ‛Fuel of the Future. Way to a Sustainable Development´┐Ż the stable communication between manufacturers, scientific institutions, regulatory authorities, road, maritime, river, rail and air transport carriers was built that give an opportunity to produce the common safety and quality concept in carrying out multimodal transports of dangerous goods ´┐Ż just the concept, which is usually discussed at all the conferences organized by the Non-Commercial Partnership ‛IDGCA´┐Ż. In the course of debate and discussion of reports topical current problems involving most often the insufficient regulatory support of transports of dangerous goods, authorization of competent bodies and determination of status of regulations released by them came up. A great discussion was given up to issues of harmonization of international standards with national ones and also manufacture of modern equipment for storage and transportation of new ecologically clean fuel types (LNG, hydrogen, ammonia, methanol). The conference participants were pleasantly impressed by favourable environment, beautiful hotel situated on the bank of Olga´┐Żs Pond, opening speech of Head of Peterhof Municipal Administration and evening informal social gathering and everything that took place this day. Forthcoming event, which the IDGCA plans to organize, will be IIIrd Meeting of Dangerous Goods Safety Advisers that will be held this October. | |
From July, 2023 the International Dangerous Goods & Containers Association will renew an issue of journal | 19.05.2023 |

Over the years from 2001 the International Dangerous Goods & Containers Association put out the bilingual journal. The journal developed the international reputation, it was well known in International Maritime Organization, UN Sub-Committee on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, international institutions and also had a lot of subscribers among Russian companies and organizations. Because of financial difficulties in the pandemia period the issue of journal was suspended and the decision was taken to renew it in July. In the first half of the year it is planned to issue two numbers and in 2024 it is scheduled to put out six issues every two months. The journal retains its own exclusivity, bilingualism and design. From June, 1, 2023, the subscription for the journal will be started. It is planned to report on the conference in the july issue and publish the most interesting papers. The work of the Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, industry committees, International Maritime Organization (IMO), International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and other organizations will be regularly highlighted. There are plans to write some columns on prevention of emergency situations, columns where opinions of scientists, experts, representatives of regulatory authorities and business. We invite all our partners, students, which took training courses in our training centre, to support the issue of the journal and enter a subscription to it. | |
Interesting discussions are expected at the Conference in Peterhof | |
|
Conference in Peterhof is expected to be interesting and advantageous for all the participants, which will gather toghether in the "New Peterhof" hotel close to the magnificent Olga's Pond. For the first time in the frame of International Conference " Multimodal Transports of Dangerous Goods" not only carriage of dangerous goods will be considered, but also problems and outlook for use of new ecologically clean types of fuel such as liquefied natural gas, hydrogen, methanol, ammonia. Although plants for LNG, hydrogen, ammonia and methanol production were already built, LNG terminals were put into operation, issues of logistics, safety, manufacture of new equipment continue to be acute on the agenda. The purpose of the Conference is to provide a background for both attending a lecture and mutual communication, exchange of views, provide the basis for signing contracts and agreements. Participation in the online mode is expected at the Conference too and those who can't be present at the hall for some reasons, will have an opportunity to address speakers and conference participants using the virtual platform. A number of leading Russian companies confirmed their attendance at the conference, among them State Corporation "Rostec", Eurochem Group AG, PAO "Cryogenmash", AO "Uralcryomash", Port "Bronka", OOO ´┐ŻLukoil-Nizhegorodnefteorgsynthez´┐Ż, OOO "Portovaya-LNG Gazprom", and also representatives of Rostechnadzor, Rostransnadzor, Federal Agency on Technical Regulation and Metrology and other. Representatives of more than 100 Russian large organizations and enterprises were invited for participation in the Conference. The event program provides for busy schedule as well as refreshment and excursion. The Conference organizer is International Staff Training Centre. Applications for participation in the Conference can be sent to e-mail addresses - istc@idgca.org, info@idgca.org. Contact telephone numbers : +7(911) 928-95-75, +7(905) 222-51-38, +7(905) 222-51-28, +7(812) 740-20-19. | |
Meeting of the Technical Committee for standardization "Oxygen and Cryogenic Equipment" (TC 114) of the Federal Agency on Technical Regulating and Metrology | 03.05.2023 |
|
On April 27, 2023 the IDGCA experts took part in the TC 114 meeting. According to the order of the day reports on the activities of the TC 114 and proposals for change in its structure and composition were considered. Oleg Bogachek, Head of the TC 114 working group "Metal-composite vessels and cylinders", came up with a suggestion on the TC structure change. Its suggestion concerned a forming the Sub-Committee SC 01 "Metal-composite vessels and cylinders" in the TC 114 on the basis of present working group. The purpose of its creation is to make the strategy in the standardization sphere for the next 5 years, development of procedures and regulations in assigned activity field, and also organization and performance of works within the frame of national, interstate (regional) and international standardization in the field in accordance with the law. This proposal as well as suggestions on the TC 114 composition change due to the incorporation of two new members and expulsion of four organizations which were disbanded and/or ceased their activities, was passed unanimously. Therefore, in the near future the order on the TC 114 "Oxygen and Cryogenic Equipment forming will be amended accordingly. | |
Ammonia requires serious approach to ensuring the transport safety | 03.05.2023 |

According to a report released on the website 47 News, on May 2, 2023 on the federal road A-180 ‛Narva´┐Ż in Kingisepp district an ammonia leakage from a tank vehicle took place. 79th fire and salvage unit team mitigated the consequences. Although the leakage according to the information source was of ‛droplet‛ nature, this event is a near-miss of more serious incident. It will be remembered that ammonia is toxic and at the same time corrosive substance, we wrote about it on our website http://www.idgca.ru/ in the section ‛News and comments´┐Ż on April 24, 2023. The information that IDGCA experts had is insufficient for carrying out of the incident cause analysis. In compliance with European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) which applied as national regulations in the Russian Federation anhydrous ammonia shall be transported as regards tank vehicles in hermetically closed tank for liquefied or dissolved gases with bottom openings for filling or discharge with three shut-off devices with minimum test pressure 26 bar (for tanks with thermal insulation) or 29 bar (for tanks without thermal insulation). For that special-purpose ‛AT vehicle´┐Ż, intended for the carriage of dangerous goods in fixed tanks or demountable tanks with a capacity exceeding 1 m3. or in tank-containers, portable tanks or multiple element gas containers (MEGCs) with an individual capacity exceeding 3 m3. Also the ADR regulations specify the requirements concerning conformity assessment procedures, inspections and tests and other. It stands to reason that in the presence of three independent shut-off devices in good working order in tank design a substance leakage even if ‛droplet´┐Ż would be hardly probable. At the forthcoming XVIIth International Conference ´┐ŻMultimodal Transports of Dangerous Goods. Fuel of the Future. Way to Sustainable Development´┐Ż which will be held on May 30, 2023, in Peterhof the emphasis will be upon issues related to ensuring the safety of transport of dangerous goods, in particular, anhydrous ammonia. Participants of the conference will get answers to the questions arising in the course of transports and storage of dangerous substances. | |
PREPARING FOR THE XVII INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE | 24.04.2023 |
|
On 30 May 2023 the XVII International Conference addressed to development of new technologies in the sphere of production and transportation of ecological fuel types will be held in Peterhof. The conference organizers provide a full information about properties of fuel new types, including dangerous in terms of their storage and carriage. Hydrogen Hydrogen is widely regarded as one of promising fuel types and already now means of transport with hydrogen engines are not rare. However, during development of technical solutions in the field of hydrogen energy it must be kept in mind the high specificity of hydrogen. There are two modifications of hydrogen - as orthohydrogen and parahydrogen. In an orthohydrogen molecule the nuclear spins (intrinsic moments of impulse) are like-directed (parallel) and in parahydrogen oppositely directed (antiparallel). In real conditions liquid hydrogen undergoes a spontaneous ortho-para conversion during its storage and transport. The ortho-para conversion carries slowly enough without catalyst and as in such a case heat release occurs, which is close in value to vaporization heat, then it is reasonable to make the catalytic conversion else at the stage of production of liquid hydrogen.Liquid hydrogen under atmospheric pressure has the boiling temperature -252,87 ?C and very low density 0,07 ´┐Ż/´┐Ż, whereby the use of hydrogen in liquid is problematic. Hydrogen may both serve as fuel in engines and be used for generation of electric power in fuel cells (chemical electric power sources), which is consumed by motors of electric vehicles. According to UN classification hydrogen is a dangerous good, hazard sub-class 2.1.(flammable gases). Hydrogen can be stored as refrigerated liquefied gas (UN 1966),in compressed condition (UN 1049) and also in metal-hydride-based storage systems (UN 3468). Liquid hydrogen shall be transported in closed and open-ended cryogenic vessels and also in portable tanks. Requirements to cryogenic vessels are specified in the instruction P203 of the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods (further UN Model Regulations) to portable tanks - in the instruction T75 with its special provisions TP5 (requirements concerning degree of filling) and TP34 (requirements to special aspects of testing for portable tanks not for rail transport). Compressed hydrogen should be transported in compliance with requirements of instruction P200 of the UN Model Regulations, which specifies that this dangerous good should be transported in tubes, cylinders, pressure drums, cylinder bundles and also multiple-element gas containers. Hydrogen in metal-hydride-based storage systems shall be transported in accordance with provisions of the instruction P205 and also with due account for special provisions 321 and 356 of the UN Model Regulations.  Methane Natural gas is rated among the most prospective energy carriers in transport, its major component (97-99%) is methane (chemical formula CH4). It can be used as fuel, but, besides that, technologies of fuel oil synthesis from it are applied, which is similar in their properties to common automobile fuels. As promising alternate fuels derived from natural gas are considered methylic alcohol (methanol), ethyl alcohol (ethanol) and dimethyl ether. By their properties mentioned alcohol fuels are suitable both for use in positive ignition engines and for their application in compression ignition engines. According to UN classification methane is a dangerous good, hazard sub-class 2.1. (flammable gases). Methane can be stored as refrigerated liquefied gas (UN 1972) and also in compressed condition (UN 1971). Liquid methane shall be transported in compliance with requirements of the same instructions as liquid hydrogen (P203 and T75). Compressed methane shall be transported in accordance with requirements of the instruction P200 of the UN Model Regulations as compressed hydrogen. Methanol Methanol (chemical formula CH3OH) is prospective alcohol fuel too, its industrial production has been mastered in many countries. But cost of methanol production in comparison with common engine fuels is much higher. Alcohol fuels have a number of significant drawbacks, among them it should be noted their toxicity (particularly with regard to methanol), corrosiveness and aggressivity to aluminium alloys, rubbers and other construction materials. According to UN classification methanol is a dangerous good, hazard class 3 (flammable liquids), its assigned number is UN 1230. Methanol in accordance with requirements of the UN Model Regulations shall be transported in packaging (instruction P001), IBC (instruction IBC02) and also portable tanks (instruction T7 with special provision TP2).  Ammonia Along with the above-mentioned there are technical proposals and developments on use of anhydrous ammonia NH3 in engines of vehicles, in particular, its mixture - 95% of ammonia and 5% of hydrogen. Such a fuel burns out with generation of water vapours and harmful nitrogen oxides (NOX), which are detoxified using the catalytic converter. This idea is quite popular although ammonia is toxic and enters into active reactions with other substances. Nevertheless it is more simple to store and transport it than hydrogen and its cost is considerably lower. Anhydrous ammonia in compliance with the UN Model Regulations has main hazard sub-class 2.3 (toxic gases) and additional hazard class 8 (corrosive substances). Ammonia according to requirements of the UN Model Regulations shall be transported in packagings (instruction P200) and in portable tanks (instruction P50).  | |
The First International Conference "Fuel of the Future. The path to sustainable development" Fuel of the future 2023. May 30, 2023, Novy Peterhof Hotel | 15.03.2023 |
Sustainable development and combating climate change are interlinked. Both goals are vital for human well-being. A more sustainable global economy built on new technologies will contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions causing climate change. This concept has been proclaimed by the UN, and many countries, including Russia, are striving for it. One of the solutions to these global problems is the transition to new fuels, and especially in all forms of transport. LNG, hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol are the most promising types of fuel. The problem of transition to new types of fuel is not only to improve the technology of production, but also to create new safe types of equipment for their storage and transportation. It is clear that all these fuels are hazardous cargoes. To ensure safety of their transportation new International Safety Standards are being developed and applied in the construction of ships as well as other types of transport and transport equipment. Maritime and river transport has advanced considerably in this direction, and it is no coincidence that the International Maritime Organization has long been a leader in this field. How to make sense of it all, which directions in the use of new types of fuel are the most promising, and how soon will that be realized? We will discuss all this at the forthcoming conference which will take place on May 30, 2023 in Peterhof. We invite representatives of companies producing different types of fuels, experts from scientific organizations, representatives of business and administrations to the conference. The operator of the conference is the International Staff Training Center. | |
| March 8 | |
|
Peace, beauty and success rest on your shoulders. Wish you happiness and good health. | |
High risk cargo: new requirements | 06.03.2023 |

In accordance with paragraph 1.4.3.1 of the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods (ST/SG/AC.10/Rev.22, UN, New York and Geneva, 2021), high-risk cargoes are cargoes that can be used not according to purpose, but for terrorist purposes and therefore lead to serious consequences, such as numerous loss of life, massive destruction or, especially for Class 7 cargo, massive social and economic disruption. Similar definitions are contained in the rules for the carriage of dangerous goods by various modes of transport (IMDG Code, ADR, ADN, RID, Annex 2 to SMGS). On February 28, 2023, Federal Law N 53-?? dated February 28, 2023 "On Amending the Federal Law "On Transport Security" and Recognizing Certain Provisions of Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation As Invalidated" came into force. This legislative act, without repealing the effect of the Federal Law ? 99-?? dated May 04, 2011 "On Licensing Certain Types of Activities" and the provisions on licensing for inland waterway and rail transport adopted as part of its implementation, clarifies the procedure for submitting high-risk cargo for transportation. According to this document the requirements to obtain special permits for transportation of high risk cargoes by railway and inland water transport as well as for transshipment of high risk cargoes in river ports are canceled. At the same time, the document provides that high-risk cargoes are allowed to be transported by railway and inland water transport vehicles if there is a notification in the form of an electronic document (message) sent to the Federal Service for Supervision in the Sphere of Transport or its territorial body using a Unified State Information System of Transport Security, and this requirement comes into force on February 29, 2024. The list of high-risk cargo was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation ? 341 dated March 10, 2022 (entered into force on March 1, 2023 and is valid until March 1, 2029). Federal Law ? 53-?? of February 28, 2023 also clarifies the procedure of implementation of measures of protection against acts of unlawful interference provided for by certificates of transport security of road transport vehicles used for transportation of dangerous goods and plans of transport security of transport infrastructure facilities used for loading, unloading and storage of high-risk cargo, as well as dangerous goods, transportation of which requires a special permit, issued in accordance with the procedure provided for in paragraph 13 of Article 11 11 of the Federal Law ? 257-?? dated November 8, 2007 "On Motor Roads and Road Activities in the Russian Federation and Amendment of Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation". | |
Specificity of transportation of paraformaldehyde (dangerous goods) | 22.02.2023 |
|
On March 1, 2023, the All-Russian intersectoral practical conference "Paraformaldehyde - 2023" will be held. Each dangerous goods listed in the UN Model Regulations has its own characteristics and specifics of packaging and transportation, and also requires careful study before it is shipped and used. The organizing committee of the conference invited the management team of IDGCA NP to participate and give a lecture. The participants will be presented with a report on the activities of IDGCA NP and the participation of the Association in improving the Regulations for the Transportation of Dangerous Goods. The report will demonstrate special conditions and hazards when working with paraformaldehyde. | |
Training of dangerous goods inspectors | 22.02.2023 |
|
The ISTC is one of the few educational institutions that trains inspectors, both in the category of civil servants and departmental ones, who are entrusted with the functions of controlling the transport of dangerous goods. For more than 15 years, the ISTC has repeatedly trained and assessed employees of Rostransnadzor, customs authorities, port control inspectors and inspectors of large Russian and foreign companies. The practice of training and retraining has shown the need for regular advanced training of the inspectors, and this is understandable, since international rules and guidelines are reissued every 2 years and new requirements are introduced into them, and sometimes new chapters. The ISTC, with the methodological assistance of IDGCA NP, updates the training programs, which makes it possible to bring the latest requirements to our students. At the end of March, the next training of inspectors under the 40-hour program is planned. Those who wish to study can send an application. | |
Risk analysis for the transport of dangerous goods | 21.02.2023 |
 
In many areas of activity related to the operation of hazardous industrial facilities, as well as the transport of dangerous goods, a risk-based approach is increasingly being used, although there are no mandatory requirements for its application in international and national legislation. Despite the tightening of the requirements of both international and national legislation in the field of transportation and handling of dangerous goods, major accidents and catastrophes with dangerous goods continue to occur, claiming human lives and causing enormous material and environmental damage. Such incidents include the explosion of ammonium nitrate in the seaport of Beirut on August 4, 2020, the fire in the port of Iskenderun in southern Turkey on February 6, 2023, the fire at the container terminal in Bangladesh on June 5, 2022, as well as the recent incident in the US state of Ohio, the consequences of which has not yet been evaluated, despite the unprecedented measures taken. Causes of accidents and disasters can be different. As a rule, they occur due to the improper technical condition of vehicles and transport equipment, violations of the rules for placing and securing cargo, etc. And, as the accident in Ohio showed, the fact of insufficient attention to the condition of main and access railway tracks can lead to large-scale negative consequences. Let's take a closer look at this incident. As it became known from a number of mass media reports, in the evening of February 3 Norfolk Southern freight train with more than a hundred cars crashed in the town of East Palestine. Several tanks contained vinyl chloride, a substance used in the production of polyvinyl chloride, a plastic widely used in various fields of engineering and construction. On February 5, local authorities decided to drain the chemical and then destroy it by incineration. Before the start of the operation, people living less than 1 mile from the crash site were evacuated. As a result of the combustion of vinyl chloride, phosgene (recall that this is a chemical warfare agent) and hydrogen chloride were thrown into the air. What is vinyl chloride? Its chemical formula is CH2=CHCl. According to UN classification VINYL CHLORIDE, STABILIZED is a dangerous substance, has UN number 1086, hazard class 2.1 - flammable gases. The boiling point of the substance is minus 13´┐ŻC, the melting point is minus 154´┐ŻC. Flash point is minus 78´┐ŻC, self-ignition temperature is 472´┐ŻC. Explosive limits in air 3.6-33 vol. %. It is highly soluble in chloroform, dichloroethane, ethanol, ether, acetone, hydrocarbons, oil and slightly in water. Safety rules for the transportation of vinyl chloride, as well as the procedure for emergency situations with this substance, are given in a number of regulatory documents. In particular, emergency card ? 205 (Emergency cards for dangerous goods transported by railways of the CIS, the Republic of Latvia, the Republic of Lithuania, the Republic of Estonia, approved by the SZHT CIS, protocol dated May 30, 2008 ? 48, as amended on November 22, 2021) prescribes in case of an incident, take the car to a safe place, isolate the danger zone within a radius of at least 200 m, correct the indicated distance based on the results of chemical reconnaissance, evacuate outsiders, and also take a number of other measures. To dissipate (isolate) the gas, use sprayed water, cover the spill site with air-mechanical foam, an inert material. The chemical reconnaissance and work managers should use portable breathing equipment (within 20 minutes). Emergency crews should use insulating gas masks and overalls. In case of fire, use flame retardant suits complete with self-rescuers. But we can see that the actions of the liquidators in Ohio were somewhat different. The reasons that led to the large-scale incident, as already noted, are still being investigated, but quite revealing was a statement by the US Railroad Workers United of America, which was published immediately after the crash: "The hallmarks of modern railroading include drastic cuts in both service and operational staff, poor customer service, deferred maintenance of rolling stock and infrastructure, long hours and chronic fatigue, limited on-the-job training, and high employee turnover." This, according to the union, could be the result of a kind of "optimization". The incident in Ohio is an example of the fact that the poor condition of transport, in this case railway, infrastructure and, most importantly, the low professional level of personnel working with dangerous goods, lead to large-scale tragic consequences. It should be noted that the Customs Union has the Technical Regulations "On the Safety of Railway Rolling Stock" (TR CU 001/2011), "On the Safety of High-Speed Rail Transport" (TR CU 002/2011) and "On the Safety of Railway Transport Infrastructure" (TR CU 003/2011), approved by the decision of the Commission of the Customs Union dated July 15, 2011 ? 710 (as amended dated October 30, 2018). Appropriate requirements are imposed on the technical characteristics of the superstructure of the railway track, on which trains with dangerous goods follow, and, in particular, on railroad rails. The training and certification of railway transport personnel is regulated by Order ? 41 of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation dated February 18, 2021 "On Approval of the Procedure and Terms for Certification of Railroad Workers and Employees Responsible for Loading, Placing, Securing Cargoes in Cars, Containers and Unloading Cargoes, as well as the Procedure of Establishment of Professional Licensing Boards", registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on May 28, 2021, registration ? 63679. The International Staff Training Center, a subsidiary of the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association, trains Russian and foreign trainees on various training programs in the field of transportation of dangerous goods. During the training, accident cases are analyzed in detail and practical recommendations are given on the application of the provisions of existing international risk management standards in the field of transport of dangerous goods. In addition, the Center implements a specialized week-long course on risk management at hazardous industrial facilities and during the transportation of dangerous goods. | |
WE TRAIN PROFESSIONALS | 24.01.2023 |
 
Qualitative advanced training of the management and engineering staff of the enterprise, whose activities are related to the operation of hazardous production facilities and the transportation of dangerous goods, is not an easy task for any educational institution. The task becomes even more challenging when students have decades of experience working at the most complex facilities, and their knowledge is at a high professional level. That is why our center carefully prepares for any courses and tries to give students something new that increases their level of professional knowledge. The relaxation in the pandemic requirements allowed the training center to conduct classes directly on the rooms of the center, which, of course, made it possible for direct communication between teachers and trainees, although it is fair to say that distance learning using modern technologies also gives trainees who are thousands of miles away from St. Petersburg a wide opportunity to listen to lectures, participate in program discussions, and take exams. From January 16 to January 20, the first classes in the new 2023 were held in St. Petersburg. Two large companies, Sakhalin Energy LTD and EuroChem Terminal Ust-Luga LTD, sent their specialists to the International Staff Training Center (ISTC) to improve their skills in handling dangerous goods and receive the title of dangerous goods advisor, which is awarded to trainees who have successfully passed exams and passed certification at the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association. Moreover, specialists from EuroChem Terminal Ust-Luga, LTD were trained online, while specialists from Sakhalin Energy, LTD were trained directly at the training center. Thanks to communication with representatives of such companies, ISTC teachers receive new information, which will be used in the future in organizing the next courses. The next training of Dangerous Goods Safety Advisors is scheduled from 13 to 17 February 2023. | |
Revised IATA Industry Standards 2023 | 20.01.2023 |

The International Air Transport Association (IATA) has announced the completion of its annual revision of its industry guidelines for cargo transportation, ground handling and operations, which has resulted in updates to many core industry standards. These changes reflect the industry's commitment to further improving safety, introducing more modern technologies, and improving the quality of passenger service and cargo handling. First of all, this concerns the With over 1.25 million shipments of dangerous goods transported by air each year, it is important that the rules and regulations that ensure the safe transport of such substances and items are reviewed to reflect changes in safety and operation. Lithium batteries have received particular attention here as consumer demand for electronic devices such as tablet PCs and small personal mobile devices continues to grow. In addition, changes have been made to the Standard Procedures for Preloading Advanced Cargo Information (PLACI), the Landing Guide for Passengers with Reduced Mobility, pet travel procedures, and the Recommendations for the Design and Operation of Systems for Preventing Collisions with Ground Support Equipment. | |
The first national standard in the field of countering terrorism | 20.01.2023 |

By order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology, a new national standard GOST R 70620-2022 "Anti-terrorist security. Terms and Definitions"" was approved. The standard recommends the main definitions in the field of anti-terrorist activities, which is very important for the general understanding and use of terminology in order to ensure a uniform interpretation of the established requirements. The document became the first Russian standard in the field of antiterrorist security. The relevance of developing a national standard in the field of ensuring the anti-terrorist protection of facilities (territories) is associated with the changes made to the legislation of the Russian Federation on countering terrorism since 2013 up to the present. | |
New transport and logistics center | 20.01.2023 |

As part of the "Formation of a network of transport and logistics centers" project, by the end of 2024, it is planned to commission the Primorsky transport and logistics center, which will be built near the Vozdvizhensky railway station near the town of Ussuriisk in Primorsky Krai. The Primorsky Center will be located near the main port infrastructure of the region and border checkpoints. A preliminary analysis showed that, taking into account the presence of a cargo base in the region, the terminal's workload is guaranteed. It is expected that the terminal will provide services for the transshipment, storage and accumulation of containerized cargo coming from the ports of Primorsky Krai, which will ensure the growth of Russia's trade turnover with the countries of the Asia-Pacific region. According to available statistics, dangerous goods account for about 20% of the total volume of goods transported in containers. In this regard, companies that are responsible for the transport of goods by several modes of transport and prepare goods for shipment need to pay special attention to the training of personnel whose activities are related to dangerous goods. Cargo can be transported both in conventional high-capacity containers and in specialized ones, including tank containers. Center (ISTC) takes into account the specifics of training specialists for multimodal operators. At the same time, the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association recommends that shippers, carriers and consignees have specialists who have been trained under the "Dangerous Goods Safety Advisor" program and undergo certification at the International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association. The presence of Advisors in the company can reduce the risk of dangerous goods incidents and will facilitate the efficient transport of dangerous goods. | |
A new mandatory safety code | 18.01.2023 |

Maritime Safety Committee (MSC 106) adopted mandatory International Code of Safety for Ships Carrying Industrial Personnel (IP Code). A new mandatory safety code for ships carrying industrial personnel - aimed at ensuring the safety of people transported to work on offshore facilities including windfarms - has been adopted by IMO's Maritime Safety Committee (MSC 106), which met from 2 to 11 November 2022. The new Chapter XV of the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) and the associated new International Code of Safety for Ships Carrying Industrial Personnel (IP Code) were developed by the IMO Sub-Committee on Ship Design and Construction (SDC 8). The aim is to provide minimum safety standards for ships that carry industrial personnel, as well as for the personnel themselves, and address specific risks of maritime operations within the offshore and energy sectors, such as personnel transfer operations. Such personnel may be engaged in the construction, maintenance, decommissioning, operation or servicing of offshore facilities, such as windfarms, as well as offshore oil and gas installations, aquaculture, ocean mining or similar activities. The amendments and Code are expected to enter into force on 1 July 2024. The International Dangerous Goods and Containers Association and the International Staff Training Centre will adjust their training programs to reflect the content of the new IMO instruments. | |
Session of the ADN Safety Committee | 18.01.2023 |
|
The forty-first session of the Joint Meeting of Experts on the Regulations annexed to the European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Inland Waterways (ADN) (ADN Safety Committee) will take place from 23 to 27 January 2023 at the Palais des Nations (Geneva). The following items are on the provisional agenda for the session:
In considering the application of ADN, the status of ADN, special permits, derogations and equivalents, the interpretation of the Regulations annexed to ADN, the training of experts, and issues relating to classification societies will be discussed. Experts of "IDGCA" NP plan to take part in the session. | |